Diversity in Living Organisms
Introduction
· Biodiversity term is used to define the diversity of life forms.
· Biodiversity is a word more often used to refer to the variety of life forms found in a particular geographic region.
· Diversity of life forms of a geographic region provides stability in the respective region.
Base of Classification
· Greek thinker Aristotle first classified animals based on their place of residence whether they lived on land, in water, or in the air.
· Later, all the living organisms are identified and categorized on the basis of their body design in form and function.
· The idea of evolution was first described by Charles Darwin in 1859 in his book namely – The Origin of Species.’
· Charles Darwin first described this idea of evolution in 1859 in his book, ‘The Origin of Species.’
Hierarchy of Classification Groups
· Some biologists, namely Ernst Haeckel (1894), Robert Whittaker (1959), and Carl Woese (1977) have attempted to classify all living organisms into broad categories and named them ‘Kingdoms.’
· Whittaker categorized into five kingdoms namely −
o Monera
o Protista
o Fungi
o Plantae
o Animalia
· Further, these kingdoms have been classification by naming the sub-groups at various levels as −
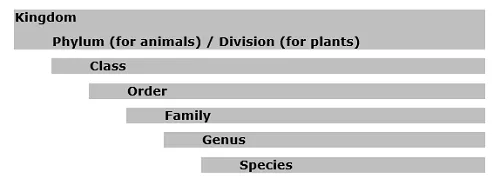
· Let’s discuss each kingdom in brief −
Monera
· The organisms of Monera kingdom do not have a defined nucleus or organelles, neither do any of them show multi-cellular body designs.
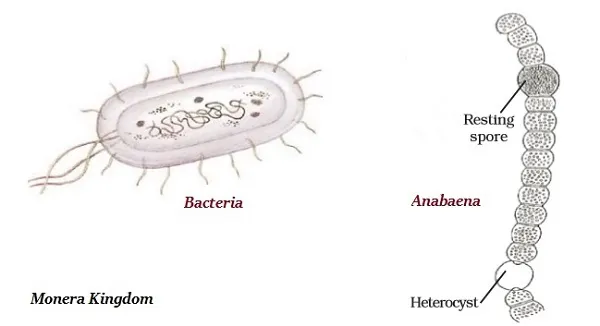
· The examples of this monera kingdom are bacteria, anabaena, blue-green algae or cyanobacteria, and mycoplasma.
Protista
· The organisms of Protista kingdom include many kinds of unicellular eukaryotic organisms.
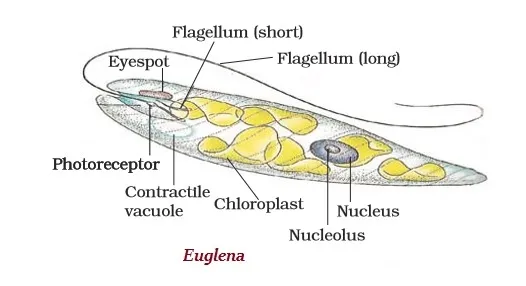
· The examples of Protista kingdom are algae, euglena, diatoms, and protozoans, etc.
Fungi
· The organisms of fungi kingdom are heterotrophic eukaryotic organisms.
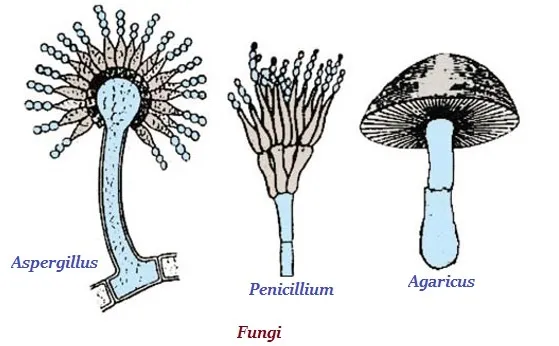
· The organisms of this kingdom use decaying organic material as their food and therefore, they are also known as saprophytes.
Plantae
· The organisms of this kingdom are multicellular eukaryotes with cell walls.
· The organisms of plantae are autotrophs and they use chlorophyll for making their food (i.e. photosynthesis).
· All plants are examples of plantae kingdom.
Animalia
· The organisms of Animalia kingdom are all organisms which are multicellular eukaryotes without cell walls.
· Organisms of Animalia kingdom are heterotrophs.