Animal Tissue
Introduction
∑ The tissue found in animals have comparatively some different properties than the plant tissue.
Types of Animal Tissue
∑ Animal Tissues are divided as −
o Epithelial Tissue
o Connective Tissue
o Muscular Tissue
o Nervous Tissue
∑ Letís discuss them in brief −
Epithelial Tissue
∑ Epithelial tissues are the covering and protective tissues in the animal body.
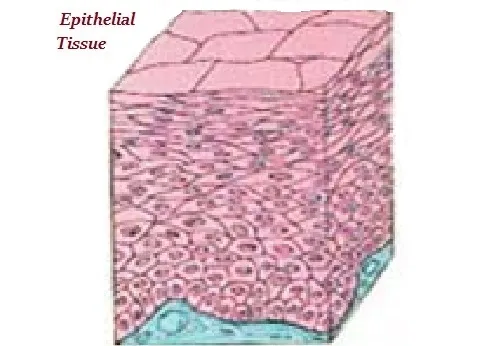
∑ Epithelial tissue covers almost all organs and cavities within the body.
∑ Epithelial tissue also forms a barrier to keep different body systems separate.
∑ Epithelial tissue cells are closely packed (as shown in the image given above) and form a continuous layer.
Connective Tissue
∑ Connective tissues are made up of the cells those are separated by non-living material, and known as an extracellular matrix.
∑ This matrix could be either liquid or rigid.
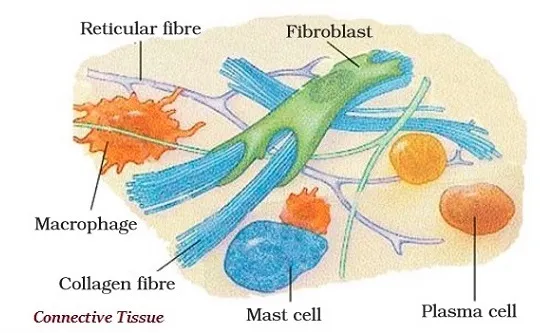
∑ Connective tissues are further divided as −
o Fibrous connective tissue
o Skeletal connective tissue and
o Fluid connective tissue
∑ Tendons are the example of fibrous connective tissue.
∑ Bone is an example of a skeletal connective tissue.
∑ Bone forms the framework and provide supports to the body.
∑ Blood is an example of fluid connective tissue.
∑ Blood has a fluid (liquid) matrix known as plasma.
∑ In plasma, the red blood cells (RBCs), the white blood cells (WBCs), and the platelets are remaining suspended.
Muscular Tissue
∑ Muscular tissue largely consists of elongated cells, and also known as muscle fibers.
∑ The muscular tissue is accountable for the movements in our body.
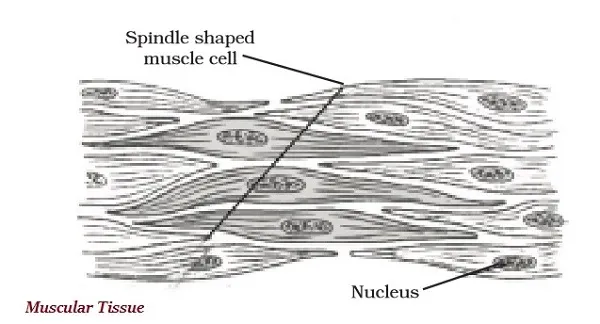
∑ The muscular tissue contains special proteins known as contractile proteins; and this protein helps in contraction and relaxation and supports free movement.
Nervous Tissue
∑ The brain, spinal cord, and nerves all are composed of the nervous tissue.
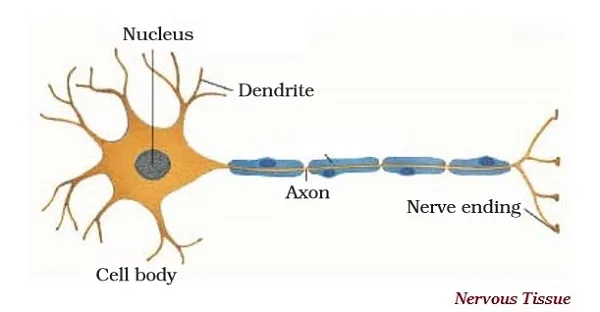
∑ Cells of the nervous tissue are extremely particular and sensitive for being stimulated and then transmitting the stimulus swiftly from one place to another within the body.
∑ The cells of nervous tissue are known as nerve cells or neurons.
∑ Nerve impulses allow us to move our muscles whenever we want to do so.