Tissues
Introduction
· A group of cells that are similar in structure and work together to accomplish a particular function is known as tissue.
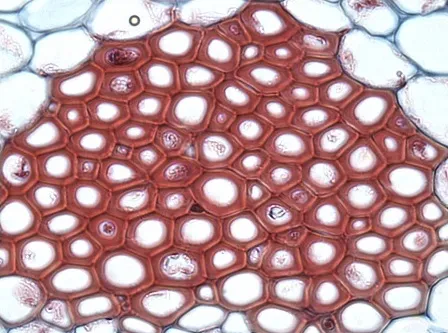
· Tissues are categorized as −
o Plant Tissue &
o Animal Tissue
· Let’s discuss them in brief −
Plant Tissue
· Following are the major types of plant tissue −
o Meristematic Tissues
o Permanent Tissues
§ Simple Permanent Tissues
§ Parenchyma
§ Collenchyma
§ Sclerenchyma
§ Epidermis
§ Complex Permanent Tissue
§ Xylem
§ Phloem
Meristematic Tissue
· Meristematic tissue mainly consists of actively dividing cells, and helps in increasing the length and thickening the stems of the plant.
· Meristematic tissue, commonly, present in the primary growth regions of a plant, for example, in the tips of stems or roots.
· Depending on the region (where the meristematic tissues are found); meristematic tissues are classified as apical, lateral, and intercalary (see the image given below).
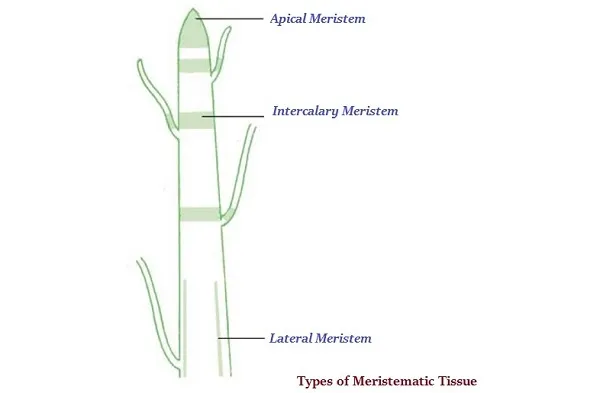
· Apical meristem (as shown in the above image) is present at the growing tips of stems and roots and helps in their growth.
· Lateral Meristem is found in stem or root region and helps in their growth.
· Intercalary meristem is found at the base of the leaves or internodes (on twigs) and helps in growth.
Permanent Tissue
· Cells of meristematic tissue later differentiate to form different types of permanent tissue.
· Permanent Tissue is further categorized as −
o Simple Permanent Tissue and
o Complex Permanent Tissue
Simple Permanent Tissue
· Simple Permanent Tissue further categorized as −
o Parenchyma
o Collenchyma
o Sclerenchyma
o Epidermis
· Parenchyma tissue provides support to plants and also stores food.
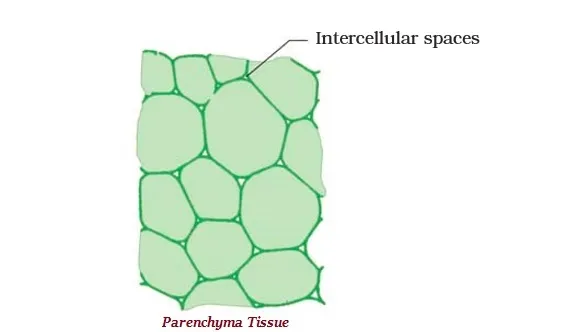
· Sometimes, parenchyma tissue contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis, in such a condition, it is known as collenchyma.
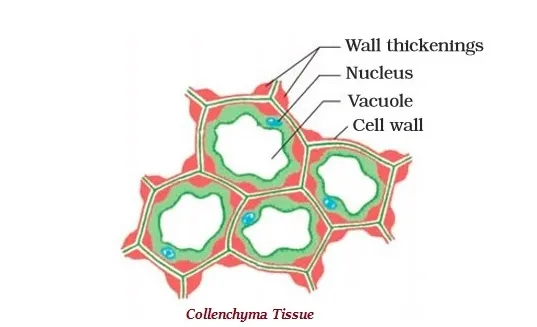
· The collenchyma tissue provides flexibility to plant and also provides mechanical support (to plant).
· The large air cavities, which are present in parenchyma of aquatic plants, give buoyancy to the plants and also help them float, are known as aerenchyma.
· The Sclerenchyma tissue makes the plant hard and stiff. For example, the husk of a coconut is made up of sclerenchymatous tissue.
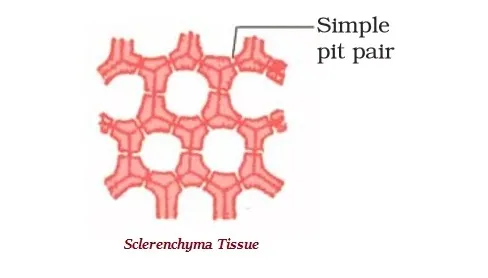
· The cells of Sclerenchyma tissue normally are dead.
· The outermost layer of cells is known as epidermis.
· The epidermis is usually made up of a single layer of cells.
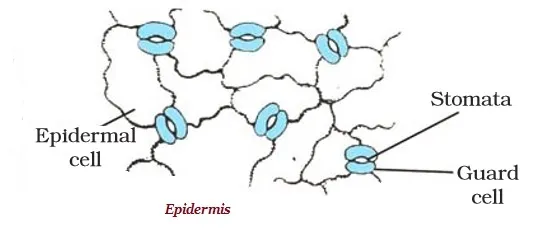
· The entire surface of a plant has the outer covering of epidermis, which protects all the parts of the plant.
Complex Permanent Tissue
· The complex tissue, normally, consists of more than one type of cells which work together as a unit.
· Complex tissues help in the transportation by carrying organic material, water, and minerals up and down in the plants.
· Complex Permanent Tissue is categorized as;
o Xylem and
o Phloem
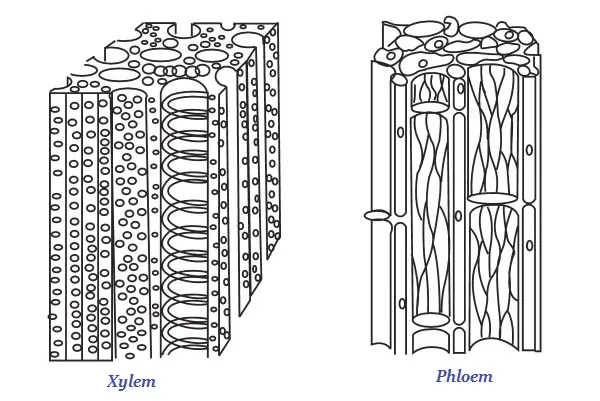
· Xylem, normally, consists of tracheid, vessels, xylem parenchyma, and xylem fibers.
· Xylem is accountable for the conduction of water and mineral ions/salt.
· Phloem, normally, is made up of four types of elements namely −
o Sieve tubes
o Companion cells
o Phloem fibers and
o Phloem parenchyma
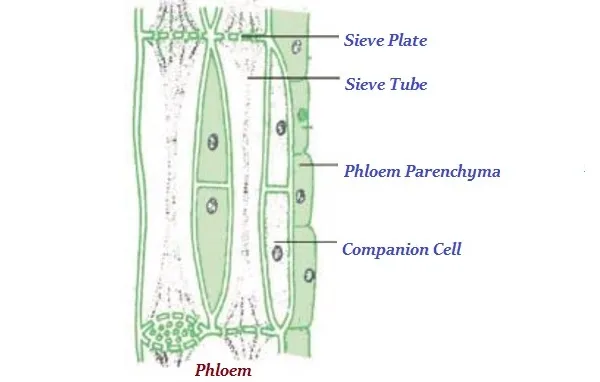
· Phloem tissue transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant.