Natural Resources
Introduction
∑ The resources, available on the Earth and the energy being received from the Sun, are essential to meet the basic necessities of all life-forms on the Earth.
∑ The biotic component incorporates all living of the biosphere.

∑ The abiotic component incorporates the air, the water, and the soil of the biosphere.
Biogeochemical Cycles
∑ Biogeochemical cycles explain a constant interaction between the biotic and abiotic components of the biosphere.
∑ Biogeochemical cycles are a dynamic phenomenon that helps to maintain the stability in the ecosystem.
∑ The significant biogeochemical cycles are −
o Water Cycle
o Carbon Cycle
o Nitrogen Cycle
o Oxygen Cycle
∑ Letís discuss each of them in brief −
Water Cycle
∑ The whole process, starting from the water evaporation, rainfall to flowing back into the sea via rivers, is known as the water-cycle.
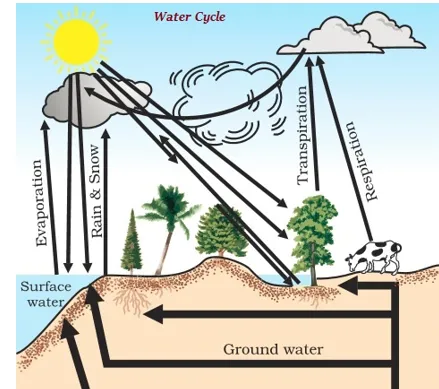
∑ As shown in the image given above, water cycle is a complex phenomenon. During the process of water cycle, it helps ecosystem by maintaining its balance.
∑ Water cycle helps in making new fertile soil, increasing the fertility of soil, providing nutrition to the biotic components in different ecological regions, etc.
Carbon Cycle
∑ Carbon is found on the Earth in various forms, such as diamond and graphite (in solid form) and in combined state i.e. carbon and dioxide (as a gas).
∑ Carbon is one of the essential elements for the photosynthesis.
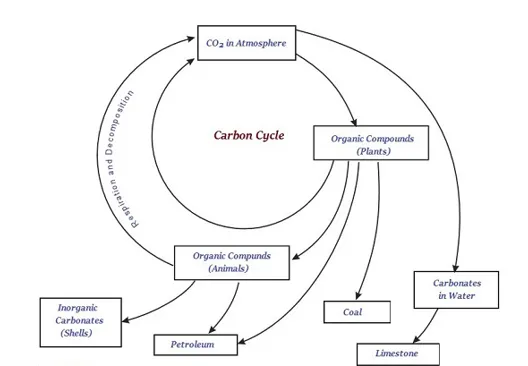
∑ The process of photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide, which is present in the atmosphere or dissolved in water into glucose molecules.
∑ The glucose provides energy to living things that involves the process of respiration.
∑ In the process of respiration, oxygen may or may not be used to convert glucose back into carbon dioxide.
∑ Lastly, the carbon dioxide goes back into the atmosphere.
Nitrogen Cycle
∑ About 78 percent part of our atmosphere is shared by nitrogen alone.
∑ Nitrogen is a part of many molecules, which are essential for the life.
∑ There are a few varieties of bacteria that help in nitrogen-fixing.
∑ These special bacteria convert the comparatively inert nitrogen molecules into nitrates and nitrites essential for the life in direct or indirect way.
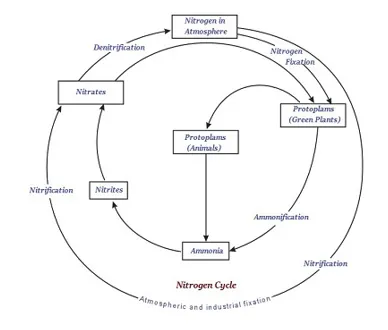
∑ The nitrogen-fixing bacteria are largely found in the roots of legumes.
Oxygen Cycle
∑ In the total constituents of our atmosphere, about 21 percent is shared by oxygen.
∑ Oxygen is also found in the Earthís crust.
∑ Oxygen is an essential component of most of the biological molecules, including carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and fats (or lipids).
∑ Oxygen, present in the atmosphere, is used especially up in the three following processes −
o Combustion
o Respiration
o Formation of oxides of nitrogen
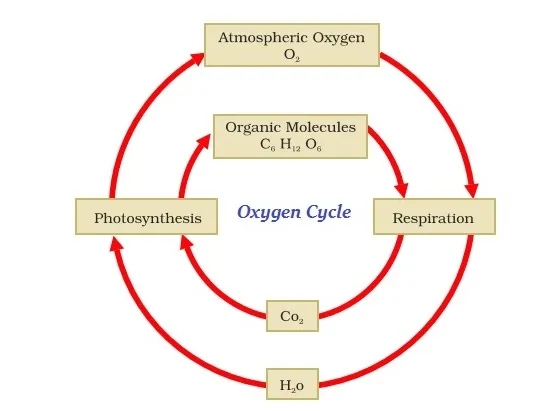
∑ Oxygen is returned back to the atmosphere by the process of photosynthesis.
∑ Oxygen is lifeline of most of the organisms found on the earth, but for some bacteria, it is poisonous.