Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
Introduction
· The living organisms (available around us), which we cannot see with our naked eyes, are known as microorganisms or microbes.
· Microorganisms are classified into the following four major groups −
o Bacteria
o Fungi
o Protozoa
o Algae
Viruses
· Viruses are also microscopic microorganism.
· Viruses get reproduced only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant, or animal.
· The common ailments, such as cold, influenza (flu), and coughs are caused by viruses.
· The serious diseases, such as polio and chicken pox are also caused by viruses.
· The diseases like dysentery and malaria are caused by protozoans.
· The diseases like typhoid and tuberculosis (TB) are caused by bacteria.
· The single celled microorganisms are known as bacteria, algae, and protozoa.
· The multicellular microorganisms are known as fungi and algae.
· The microorganism can survive in any type of environment ranging from ice cold to hot desert.
· Microorganisms are also found in the bodies of animals and human beings.
· Microorganisms, such as amoeba, can live alone; whereas the fungi and bacteria live in colonies.
· Some of the microorganisms are beneficial to us in many ways whereas some others are harmful and cause diseases to us.
Friendly Microorganisms
· Microorganisms are used for various purposes, such as preparation of curd, bread, cake; production of alcohol; cleaning up of the environment; preparation of medicines; etc.
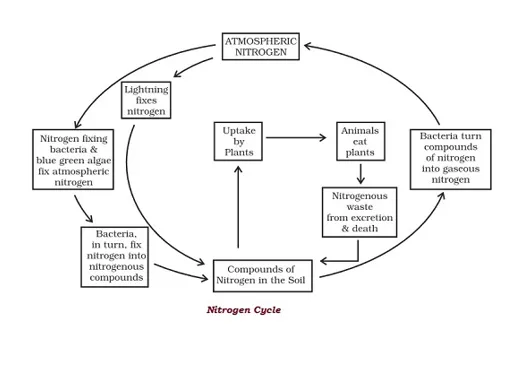
· In agriculture, microorganisms are used to increase soil fertility by nitrogen fixation.
· The bacterium lactobacillus helps in the formation of curd.
· The microorganisms, yeast is used for the commercial production of alcohol and wine.
· For the large scale use of yeast, it is grown on natural sugars present in grains like wheat, barley, rice, crushed fruit juices, etc.
· The process of conversion of sugar into alcohol (by yeast) is known as fermentation.
· Streptomycin, tetracycline, and erythromycin are some of the commonly used antibiotics; these are made from fungi and bacteria.
· These days, antibiotics are mixed with the feed of livestock and poultry that check microbial infection in the animals.
· Several diseases, such as cholera, tuberculosis, smallpox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination.
· In 1798, Edward Jenner discovered the vaccine for smallpox.
Harmful Microorganisms
· The microorganisms that cause diseases to human beings, animals, and plants, are known as pathogens.
· Pathogens enter into humans’ body through the air while breathing, the water while drinking, or the food while eating.
· Some pathogens are transmitted by direct contact with an infected person or carried through an animal.
· The microbial diseases that normally spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food or physical contact are known as communicable diseases. E.g. cholera, common cold, chicken pox, tuberculosis, etc.
· Female Anopheles mosquito carries the parasite of malaria and known as carrier.
· Female Aedes mosquito carries the parasite of dengue virus.
Human Diseases
· The following table illustrates some Common Human Diseases caused by Microorganisms –
|
Human Disease |
Causative Microorganism |
Mode of Transmission |
|
Tuberculosis |
Bacteria |
Air |
|
Measles |
Virus |
Air |
|
Chicken Pox |
Virus |
Air/Contact |
|
Polio |
Virus |
Air/Water |
|
Cholera |
Bacteria |
Water/Food |
|
Typhoid |
Bacteria |
Water |
|
Hepatitis B |
Virus |
Water |
|
Malaria |
Protozoa |
Mosquito |
Microorganisms causing Disease in Animals
· In 1876, Robert Köch discovered the bacterium (Bacillus anthracis), which causes anthrax disease.
· Anthrax, a dangerous disease caused by a bacterium, affects both human and cattle.
· Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by a virus.
· The following table illustrates some Common Plant Diseases caused by Microorganisms –
|
Plant Disease |
Causative Microorganism |
Mode of Transmission |
|
Citrus canker |
Bacteria |
Air |
|
Rust of wheat |
Fungi |
Air, seeds |
|
Yellow vein mosaic of bhindi (Okra) |
Virus |
Insects |
Food Preservation
· Salts and edible oils are the common chemicals usually used to check the growth of microorganisms, they are known as preservatives.
· Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are also used as common preservatives.
· Common salt is usually used to preserve meat and fish for ages.
· Sugar reduces the moisture content, which prevents the growth of bacteria; therefore, Jams, jellies, and squashes are preserved by sugar.
· Use of oil and vinegar averts spoilage of pickles, as bacteria cannot live in such kind of environment.
· When the milk is heated at about 700C for 15 to 30 seconds and then swiftly chilled and stored; the process prevents the growth of microbes. This process was conceptualized by Louis Pasteur; therefore, it is known as pasteurization.
Nitrogen Cycle