Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Introduction
· The phase of life, when the body undergoes radical changes, leading to reproductive maturity, is known as adolescence.
· Adolescence normally begins around the age of 11 and lasts up to 18 or 19 years of the age. However, the phase of adolescence varies from person to person.
· Starting from thirteen (13) to nineteen (19), ‘teen’ is suffix and common in every number; therefore, adolescents are also known as ‘teenagers.’
· In girls, adolescence phase may begin one year or two years earlier than the boys.
· During the adolescence phase, the human body undergoes several changes, which are marked as the onset of puberty.
· The most important change, which marks puberty, is that the boys and the girls become capable of reproduction.
· Puberty, however, ends when an adolescent phase attains reproductive maturity.
Changes at Puberty
· The most conspicuous change during the puberty is the swift increase in height.
· In the beginning, girls grow faster than boys, but by reaching 18 years of the age, both attain their maximum height.
· The rate of body growth (in terms of height) varies from person to person.
· The changes occurring in adolescent boys and girls are also much different.
· At puberty, especially the boys’ voice boxes or the larynxes begin to grow and develop larger voice boxes.
· The growing larynxes in boys can be seen as a protruding part of the throat; it is known as Adam’s apple.
· In girls, the larynx is small; hence, it is not visible from the outside.
· Adolescence is also the phase of change in a person’s way of thinking.
· Hormones, which are the chemical substances, are responsible for the changes in adolescence.
· The testes (in boys), at the onset of puberty, release testosterone hormone.
· Once puberty is reached in girls, ovaries begin to produce the hormone namely estrogen; it is responsible to the breasts develop.
· Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream.
· In the body, there are many endocrine glands or ductless glands.
· The sex hormones are under the control of hormones released by the pituitary gland.
Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans
· At puberty, the released egg (in women), and the thickened lining of the uterus along with its blood vessels get shed off in the form of bleeding known as menstruation.
· The first menstrual flow begins at puberty and is known as menarche.
· Menstruation occurs once in about 28 to 30 days.
· By the age of 45 to 50 years, the menstrual cycle stops, which is known as menopause.
· The thread-like structures in the fertilized egg are known as chromosomes.
· All human beings have 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in the nuclei of their cells.
· In boys, out of 23 pairs of chromosomes, two chromosomes named X and Y are the sex chromosomes.
· In girls, out of 23 pairs of chromosomes, two chromosomes named X and X are the sex chromosomes.
· When a sperm carrying X chromosome fertilizes with the egg, the zygote would have two X chromosomes that develop into a female child (as shown in the image given below).
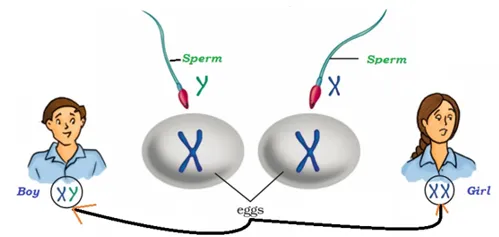
· When a sperm carrying Y chromosome fertilizes with the egg, the zygote would have two chromosomes i.e. X and Y and such zygote develops into a male child (as shown in the image given above).