Structure and Functions
Introduction
· The basic structural unit of an organ is known as the cell.
· In 1665, Robert Hooke discovered the cell.
· A cell is a living organism.
· A human body has trillions of cells, which vary in shapes and sizes.
· The organism, which is made up of more than one cell, is known as multicellular organism.
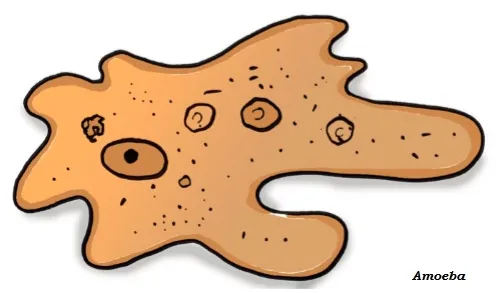
· The single-celled organisms are known as unicellular organism. E.g. Amoeba.
· A single-celled organism performs all the essential functions that a multicellular organism performs.
· Unlike other organisms, Amoeba has no definite shape; so, it keeps on changing its shape.
· Amoeba has pseudopodia, which means – pseudo means false and podia means feet.
· Amoeba is a full-fledged organism capable of independent existence.
· Shape of the cells are normally round, spherical, or elongated.
· Protoplasm is known as the living substance of the cell.
· The cells having nuclear substances without nuclear membrane are known as prokaryotic cells. E.g. bacteria and blue green algae.
· The cells having well organized nucleus with a nuclear membrane are designated as eukaryotic cells. All multicellular organisms are eukaryotic cells.
Cell Structure and Function
· The basic parts of a cell are cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
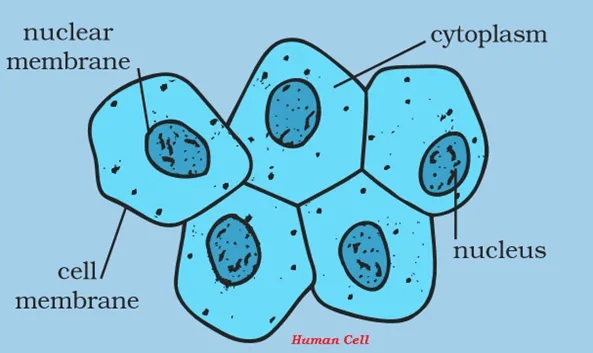
· Cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane.
· The plasma membrane is porous and allows certain substances or materials move both inward and outward.
· The central dense round structure in the center is known as nucleus.
· The jelly-like substance between the nucleus and the cell membrane (as shown in the above image) is known as cytoplasm.
· Different organelles of cells are also present in the cytoplasm such as Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, Ribosomes, etc.
· Located in central part, nucleus is almost in spherical shape.
· Nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a porous membrane known as the nuclear membrane.
· The smaller and spherical structure, found inside the nucleus, is known as nucleolus.
· Nucleus contains thread-like structures known as chromosomes.
· Chromosomes carry genes and help in inheriting the characteristics of the parents to the offspring.
· Gene is a fundamental unit of inheritance in living organisms.
· The entire constituents of a living cell are known as protoplasm, which include nucleus and cytoplasm.
Plant Cell
· The cell membrane provides shape to the cells of plants and animals.
· In plant cell, cell wall is an additional covering over the cell membrane.
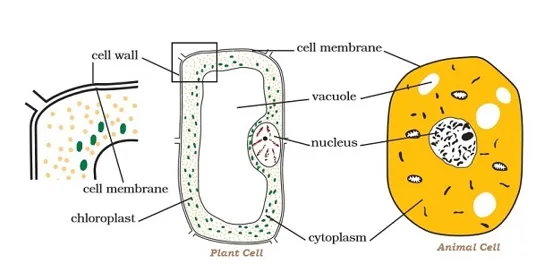
· An animal cell does not have cell wall.
· Cell wall gives shape and rigidity to plant cells.
· Cell wall gives protection, plant cells need protection against varying temperature, high wind speed, atmospheric moisture, etc.
· Bacterial cell also has a cell wall.
· Usually, most of the cells are microscopic in size and are not visible to the naked eye.
· The size of smallest cell is 0.1 to 0.5 micrometer found in bacteria.
· The size of largest cell is 170 mm × 130 mm, found in the egg of an ostrich.
· The size of the cells however has no relation with the size of the body of the animal or plant.
· Some small colored bodies in the cytoplasm of the cells of Tradescantia leaf are known as plastids.
· Plastids are found in different colors.
· Some plastids have green pigment and known as chlorophyll.
· Green colored plastids are known as chloroplasts.
· Chloroplasts give green color to the leaves.
· Chlorophyll is essential for the photosynthesis.