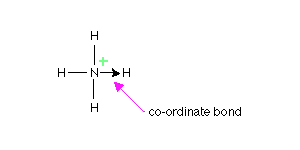
Co-ordinate Bond
Co-ordinate bond is a type of alternate covalent bond that is formed by sharing of electron pair from a single atom. Both shared electrons are donated by the same atom. It is also called dative bond or dipolar bond.
Co-ordinate covalent bonds are usually formed in reactions that involve two non-metals such as a hydrogen atom or during bond formation between metals ions and ligands.
Below we have given a simple diagram of a co-ordinate bond. The bond is shown by an arrow which points in the direction where an atom is donating the lone pair to the atom that is receiving it.

Here are a few examples of the coordinate covalent bond.
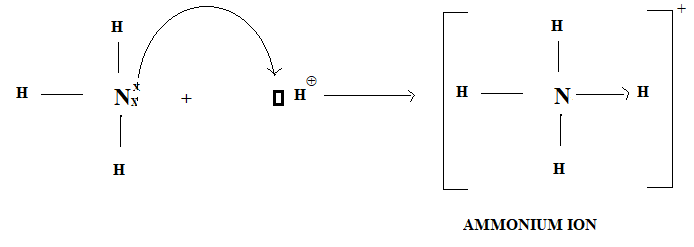
The nitrogen atom in Ammonia donates its electron pair to the empty orbital of H+ ion thus nitrogen is donor, H+ is acceptor and a co-ordinate bond is formed
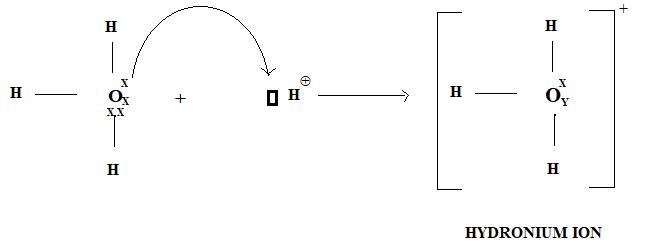
An oxygen atom in water donates its one pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of H+ ion thus a dative bond is formed oxygen atom is donor atom and H+ acceptor atom
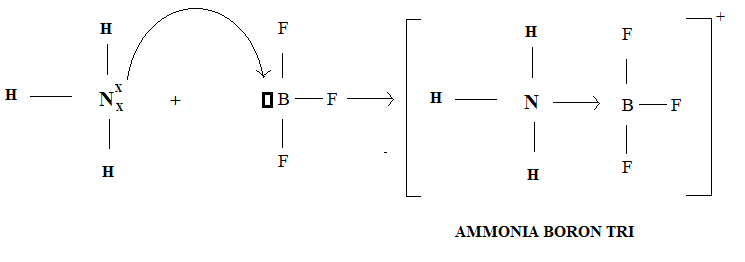
The nitrogen atom in Ammonia donates one pair of electrons to the vacant orbital of Boron atom in Boron trifluoride thus nitrogen atom is donor atom and boron atom is acceptor.