Bond Characteristics
Bond Length
During chemical bonding, when the atoms come closer to each other, the attraction takes place between them and the potential energy of the system keeps on decreasing till a particular distance at which the potential energy is minimum. If the atoms come more closer, repulsion starts and again the potential energy of the system begins to increase.
At equilibrium distance, the atoms keep on vibrating about their mean position. The equilibrium distance between the centres of the nuclei of the two bonded atoms is called its Bond length.
It is expressed in terms of an angstrom (A0) or picometer (pm). It is determined experimentally by x-ray diffraction or electron diffraction method or spectroscopic method. The bond length in chemical bonding is the sum of their ionic radii, in an ionic compound. In a covalent compound, it is the sum of their covalent radii. For a covalent molecule AB, the bond length is given by d= ra + rb
Factors Affecting the Bond length
Bond Enthalpy
When atoms come close together the energy is released due to the chemical bonding between them. The amount of energy required to break one mole of bonds of a type so as to separate the molecule into individual gaseous atoms is called bond dissociation enthalpy or Bond enthalpy. Bond enthalpy is usually expressed in KJ mol-1.
Greater is the bond dissociation enthalpy, greater is the bond strength. For diatomic molecules like H2, Cl2, O2, N2, HCl, HBr, HI the bond enthalpies are equal to their dissociation enthalpy.
In the case of polyatomic molecules, bond enthalpies are usually the average values, because the dissociation energy varies with each type of bond.
In H20, first O-H bond enthalpy = 502 KJ/mol; Second bond enthalpy = 427 KJ/mol Average bond enthalpy = (502 + 427) / 2 = 464.5 KJ/mol
Factors Affecting Bond Enthalpy in Chemical Bonding
Size of the Atom
Greater the size of the atom, greater is the bond length and less is the bond dissociation enthalpy i.e. less is the bond strength during chemical bonding.
Multiplicity of Bonds
Greater is the multiplicity of the bond, greater is the bond dissociation enthalpy.
Number of Lone Pair of Electrons Present
More the number of lone pair of electrons present on the bonded atoms, greater is the repulsion between the atoms and thus less is the bond dissociation enthalpy of the chemical bond.
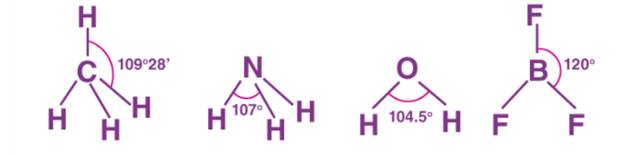
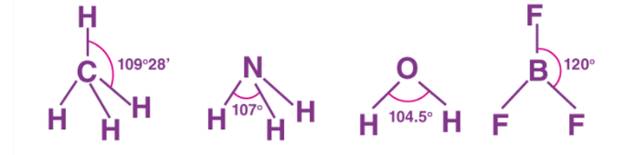
Bond Angle
A bond is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. The direction of overlap gives the direction of the bond. The angle between the lines representing the direction of the bond i.e. the orbitals containing the bonding electrons is called the bond angle.