Types of Chemical Bonds
When substances participate in chemical bonding and yield compounds, the stability of the resulting compound can be gauged by the type of chemical bonds it contains.
The type of chemical bonds formed vary in strength and properties. There are 4 primary types of chemical bonds which are formed by atoms or molecules to yield compounds. These types of chemical bonds include:
These types of bonds in chemical bonding are formed from the loss, gain, or sharing of electrons between two atoms/molecules.
Ionic Bonding
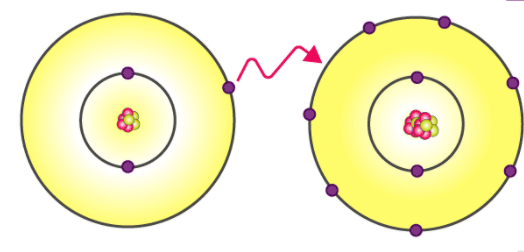
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding which involves a transfer of electrons from one atom or molecule to another. Here, an atom loses an electron which is in turn gained by another atom. When such an electron transfer takes place, one of the atoms develops a negative charge and is now called the anion.
The other atom develops a positive charge and is called the cation. The ionic bond gains strength from the difference in charge between the two atoms, i.e. the greater the charge disparity between the cation and the anion, the stronger the ionic bond.

A covalent bond indicates the sharing of electrons between atoms. Compounds that contain carbon (also called organic compounds) commonly exhibit this type of chemical bonding. The pair of electrons which are shared by the two atoms now extend around the nuclei of atoms, leading to the creation of a molecule.
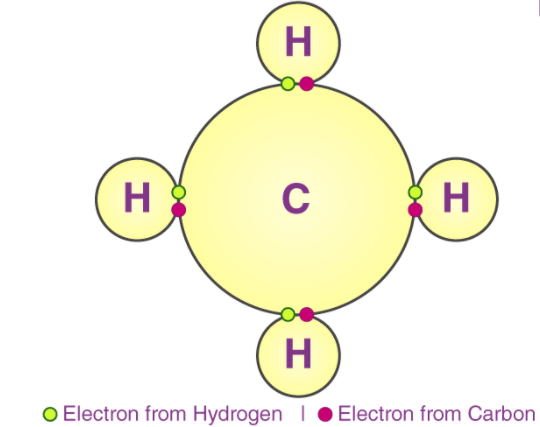
Covalent bonds can be either be Polar or Non-Polar in nature. In Polar Covalent chemical bonding, electrons are shared unequally since the more electronegative atom pulls the electron pair closer to itself and away from the less electronegative atom. Water is an example of such a polar molecule.
A difference in charge arises in different areas of the atom due to the uneven spacing of the electrons between the atoms. One end of the molecule tends to be partially positively charged and the other end tends to be partially negatively charged.
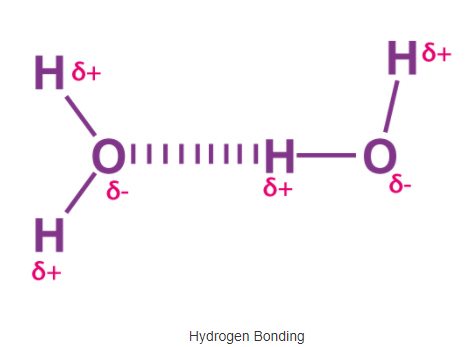
Compared to ionic and covalent bonding, Hydrogen bonding is a weaker form of chemical bonding. It is a type of polar covalent bonding between oxygen and hydrogen wherein the hydrogen develops a partial positive charge. This implies that the electrons are pulled closer to the more electronegative oxygen atom.
This creates a tendency for the hydrogen to be attracted towards the negative charges of any neighbouring atom. This type of chemical bonding is called a hydrogen bond and is responsible for many of the properties exhibited by water.