NUCLEOTIDES
Nucleotides are the basic monomer building block units in the nucleic acids. A nucleotide consists of a phosphate, pentose sugar, and a heterocyclic amine.
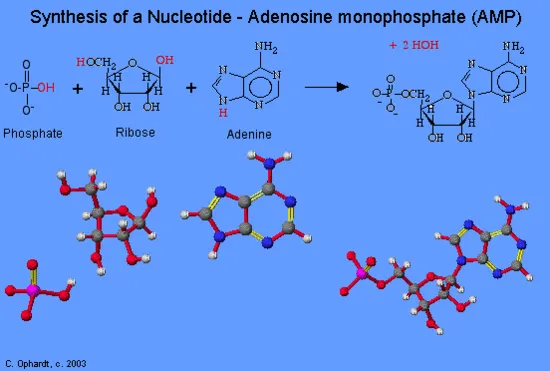
Adenosine 5'-monophosphate (AMP)
The phosphoric acid forms a phosphate-ester bond with the alcohol on carbon #5 in the pentose. A nitrogen in the heterocyclic amines displaces the -OH group on carbon #1 of the pentose. The reaction is shown in the graphic below. If the sugar is ribose, the general name is ribonucleotide and deoxyribonucleotide if the sugar is deoxyribose. The other four nucleotides are synthesized in a similar fashion.
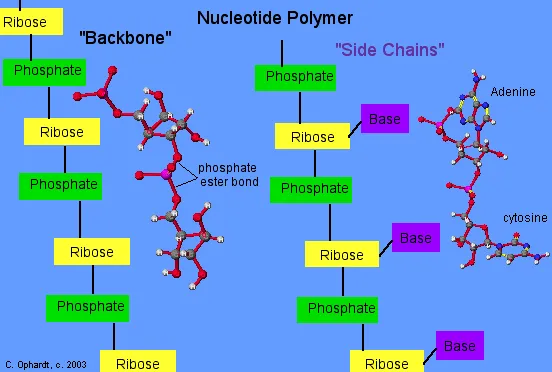
Polymeric Nucleotides
· The primary structure of both DNA and RNA consists of a polymeric chain of nucleotides. The formation of the polymeric nucleotides follows the polyester synthesis principle. The nucleotides are joined together by phosphate-ester bonds between the -OH on carbon #3 of one pentose and the -OH on carbon #5 of the next pentose which is referred to as the 3'-5' phosphate linkage. An example of a partial primary structure for a fragment of RNA is shown in the graphic on the left.
· The backbone structure for either DNA or RNA is the alternating pentose sugar and phosphate units. The heterocyclic amines or bases which are part of this polymeric structure are said to be "side chains" off of the "backbone" structure.
·
The backbone
for RNA as shown is alternating phosphate - ribose -
phosphate - ribose - etc. The possible bases are adenine, cytosine, guanine, and
uracil. DNA Single Strand - 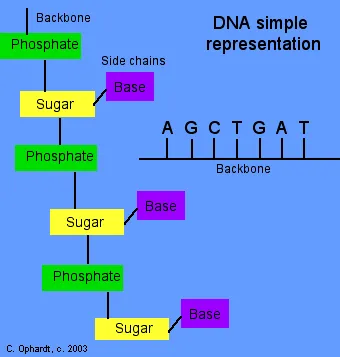
Simple Representation of Nucleotide Polymer
There are a variety of simple ways to represent the primary structures of DNA and RNA. The simplest method is just a simple line to indicate the pentose-phosphate backbone with letters to indicate the heterocyclic amines as shown in the graphic on the left.
Just as the exact amino acid sequence is important in proteins, the sequence of heterocyclic amine bases determines the function of the DNA and RNA. This sequence of bases on DNA determines the genetic information carried in each cell. Currently, much research is under way to determine the heterocyclic amine sequences in a variety of RNA and DNA molecules. The Genome Project as already succeeded in determining the DNA sequences in humans and other organisms. Future research will be to determine the exact functions of each DNA segment as these contain the codes for protein synthesis.