Can You Control Enzymes?
 Good
question! We know what you're thinking: "What if enzymes just kept going
and converted every molecule in the world? They would never stop.
They would become monsters!" Donít worry. An organism can create its own
molecules to slow down and stop the activity of enzymes and proteins. At other
times, enzymes can by controlled by poisons and contaminants, such as
herbicides. There are many factors that can regulate enzyme activity, including
temperature, activators, pH levels,
and inhibitors.
Good
question! We know what you're thinking: "What if enzymes just kept going
and converted every molecule in the world? They would never stop.
They would become monsters!" Donít worry. An organism can create its own
molecules to slow down and stop the activity of enzymes and proteins. At other
times, enzymes can by controlled by poisons and contaminants, such as
herbicides. There are many factors that can regulate enzyme activity, including
temperature, activators, pH levels,
and inhibitors.
Temperature: That's a good one. Proteins change
shape as temperatures change. Because so much of an enzyme's activity is based
on its shape, temperature changes can mess up the process and the enzyme won't
work. High enough temperatures will cause the enzyme to denature and have its
structure start to break up.
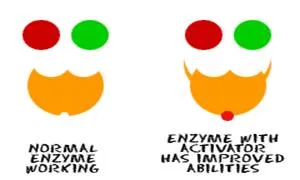
Activators: Sometimes you need an enzyme to work faster.
Your body can then create activators. At other times, you might eat something
that plays the role of an activator. Activators make enzymes work harder and
faster. If you're running in a race and you need more energy, get those enzymes
to work! Hormones can
trigger responses that activate enzymes.
 pH Levels: The acidity of
the environment changes the shape of proteins in the same way that temperature
does. Do you remember that pH is
a measure of acidity? An increased acidity near an enzyme can cause its shape
to change. Those polar and nonpolar amino acids start to twist. If
there is enough of a change, the protein could unravel and become totally
ineffective.
pH Levels: The acidity of
the environment changes the shape of proteins in the same way that temperature
does. Do you remember that pH is
a measure of acidity? An increased acidity near an enzyme can cause its shape
to change. Those polar and nonpolar amino acids start to twist. If
there is enough of a change, the protein could unravel and become totally
ineffective.
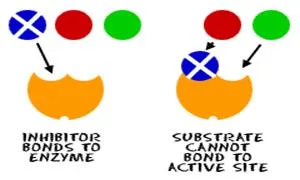
Inhibitors: These are the opposite of activators. Inhibitors
either slow down or stop the activity of an enzyme. They
often bond to the protein, changing the overall shape of the enzyme.
Remember, when the shape changes, the enzyme will not work the same way. A
nasty example of an inhibitor is snake venom or maybe nerve gas from World
War I.