ZONE ROUTING PROTOCOL (ZRP)
The Zone Routing Protocol (ZRP) was introduced in 1997 by Haas and Pearlman.
It is either a proactive or reactive protocol. It is a hybrid routing protocol.
It combines the advantages from proactive and reactive routing.
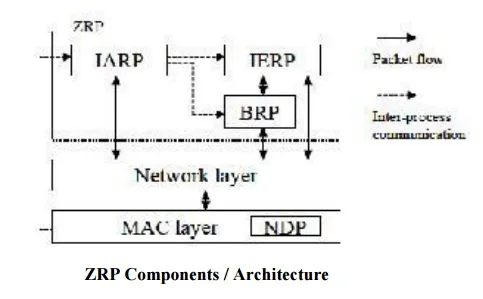
It takes the advantage of pro-active discovery within a node's local neighborhood (Intra zone Routing Protocol (IARP)), and using a reactive protocol for communication between these neighborhoods (Inter zone Routing Protocol(IERP)).
The Broadcast Resolution Protocol (BRP) is responsible for the forwarding of a route request.
ZRP divides its network in different zones.
Each node may be within multiple overlapping zones, and each zone may be of a different size.
The size of a zone is not determined by geographical measurement. It is given by a radius of length, where the number of hops is the perimeter of the zone. Each node has its own zone.
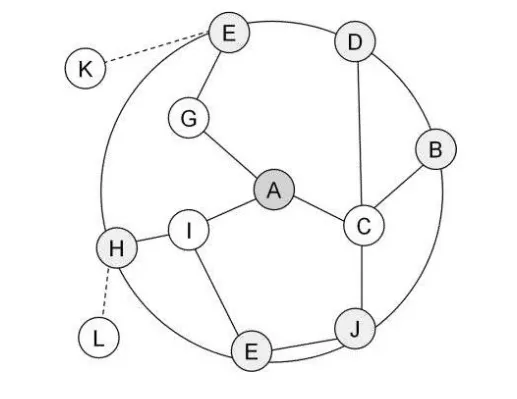
Example

radius=2-Hop; E, D, B, J, E and H are border-nodes
Illustration
Before constructing a zone and determine border nodes , a node needs to know about its local neighbors.
A node may use the media access control (MAC) protocols to learn about its direct neighbors. It also may require a Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP).
ZRP does not strictly specify the protocol used but allows for local independent implementations.
NDP relies on the transmission of hello messages by each node.
When the node, for example node A, gets a response from a node B which has received the "Hello"-messages, the node A notice that it has a direct point-to-point connection with that node B.
The NDP selects nodes on various criteria, e.g.:
1. signal strength
2. frequency/delay of beacons.
Once the local routing information has been collected, the node periodically broadcasts discovery messages in order to keep its map of neighbours up to date.
Sometimes the MAC layer of the nodes does not allow for such a NDP.
Components of ZRP
The Zone Routing Protocol consists of several components, which only together provide the full routing benefit to ZRP
Even though the hybrid nature of the ZRP seems to indicate that it is a hierarchical protocol, it is important to point out that the ZRP is in fact a flat protocol.
ZRP is more efficiency for large networks
Advantage
Less control overhead as in a proactive protocol or an on demand protocol
Disadvantages
Short latency for finding new routes