Bluetooth
Introduction
Bluetooth wireless technology is a short-range radio technology, which is developed for Personal Area Network (PAN). Bluetooth is a standard developed by a group of electronics manufacturers that allows any sort of electronic equipment -- from computers and cell phones to keyboards and headphones -- to make its own connections, without wires, cables or any direct action from a user. It is an ad hoc type network operable over a small area such as a room. Bluetooth wireless technology makes it possible to transmit signals over short distances between telephones, computers and other devices and thereby simplify communication and synchronization between devices. It is a global standard that:
· Eliminates wires and cables between both stationary and mobile devices
· Facilitates both data and voice communication
· Offers the possibility of ad hoc networks and delivers the ultimate synchronicity between all your personal devices
Bluetooth is a dynamic standard where devices can automatically find each other, establish connections, and discover what they can do for each other on an ad hoc basis. Bluetooth is intended to be a standard that works at two levels:
· It provides agreement at the physical level -- Bluetooth is a radio-frequency standard.
· It also provides agreement at the next level up, where products have to agree on when bits are sent, how many will be sent at a time and how the parties in a conversation can be sure that the message received is the same as the message sent.
It is conceived initially by Ericsson, before being adopted by a myriad of other companies, Bluetooth is a standard for a small, cheap radio chip to be plugged into computers, printers, mobile phones, etc. A Bluetooth chip is designed to replace cables by taking the information normally carried by the cable, and transmitting it at a special frequency to a receiver Bluetooth chip, which will then give the information received to the computer, phone whatever.
Topology
There are two types of topology for Bluetooth – Piconet, Scatter net. The Piconet is a small ad hoc network of devices (normally 8 stations) as shown in Fig. 5.8.1. It has the following features:
· One is called Master and the others are called Slaves
· All slave stations synchronizes their clocks with the master
· Possible communication - One-to-one or one-to-many
· There may be one station in parked state
· Each piconet has a unique hopping pattern/ID o Each master can connect to 7 simultaneous or 200+ inactive (parked) slaves per piconet
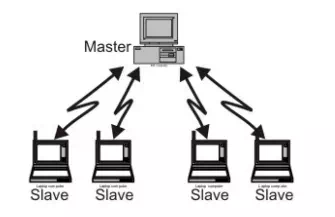
Figure Piconet topology of Bluetooth
By making one slave as master of another Piconet, Scatter net is formed by combining several Piconets as shown in Fig. 5.8.2. Key features of the scatter net topology are mentioned below:
· A Scatter net is the linking of multiple co-located piconets through the sharing of common master or slave devices.
· A device can be both a master and a slave.
· Radios are symmetric (same radio can be master or slave).
· High capacity system, each piconet has maximum capacity (720 Kbps)
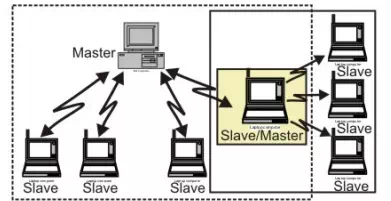
Figure ; Scatternet topology