TURBOCHARGER
A turbocharger or turbo is a forced induction
device used to allow more power to be produced for an engine of a given size. A
turbocharged engine can be more powerful and efficient than a naturally
aspirated engine because the turbine forces more intake air, proportionately
more fuel, into the combustion chamber than if atmospheric pressure alone is
used. Turbo are commonly used on truck, car, train, and construction equipment
engines. Turbo are popularly used with Otto cycle and Diesel cycle internal combustion
engines.
There are two ways of increasing the power of
an engine. One of them would be to make the fuel-air mixture richer by adding
more fuel. This will increase the power but at the cost of fuel efficiency and
increase in pollution levels… prohibitive! The other would be to somehow
increase the volume of air entering into the cylinder and increasing the fuel
intake proportionately, increasing power and fuel efficiency without hurting
the environment or efficiency. This is exactly what Turbochargers do,
increasing the volumetric efficiency of an engine.
In a naturally aspirated engine, the downward
stroke of the piston creates an area of low pressure in order to draw more air
into the cylinder through the intake valves. Now because of the
pressure in the cylinder cannot go below 0 (zero) psi (vacuum) and relatively
constant atmospheric pressure (about 15 psi) there will be a limit to the
pressure difference across the intake valves and hence the amount of air
entering the combustion chamber or the cylinder. The ability to fill the
cylinder with air is its volumetric efficiency. Now if we can increase the
pressure difference across the intake valves by some way we can make more air
enter into the cylinder and hence increasing the volumetric efficiency of the
engine.
It increases the pressure at the point where
air is entering the cylinder, thereby increasing the pressure difference across
the intake valves and thus more air enters into the combustion chamber. The
additional air makes it possible to add more fuel, increasing the power and
torque output of the engine, particularly at higher engine speeds.
Turbochargers were originally known as Turbo
superchargers when all forced induction devices were classified as
superchargers; nowadays the term "supercharger" is usually applied to
only mechanically-driven forced induction devices. The key difference between a
turbocharger and a conventional supercharger is that the latter is mechanically
driven from the engine, often from a belt connected to the crankshaft, whereas
a turbocharger is driven by the engine's exhaust gas turbine. Compared to a
mechanically-driven supercharger, turbochargers tend to be more efficient but
less responsive.
HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
The turbocharger was invented by Swiss
engineer Alfred Büchi. His patent for a turbocharger was applied for use in
1905. Diesel ships and locomotives with turbochargers began appearing in the
1920s.
AVIATION:
During the First World War French
engineer Auguste Rateau fitted
turbochargers to Renault engines powering various French fighters with some
success. In1918, General Electric engineer Sanford Moss attached a turbo to a
V12 Liberty aircraft engine. The engine was tested at Pikes Peak in Colorado at
4,300 m to demonstrate that it could eliminate the power losses usually
experienced in internal combustion engines as a result of reduced air pressure
and density at high altitude.
Turbochargers were first used in production
aircraft engines in the 1920s, although they were less common than
engine-driven centrifugal superchargers. The primary purpose behind most
aircraft-based applications was to increase the altitude at which the airplane
could fly, by compensating for the lower atmospheric pressure present at high
altitude.
PRODUCTION AUTOMOBILES:
The first turbocharged diesel truck was
produced by Schweizer Maschinenfabrik Saurer(Swiss Machine Works Saurer) in 1938 .The first production turbocharged automobile
engines came from General Motors in 1962. At the Paris auto show in1974, during
the height of the oil crisis, Porsche introduced the 911 Turbo – the world’s
first production sports car with an exhaust turbocharger and pressure
regulator. This was made possible by the introduction of a waste gate to direct
excess exhaust gasses away from the exhaust turbine. The world's first
production turbo diesel automobiles were the Garrett-turbocharged Mercedes
300SD and the Peugeot 604, both introduced in 1978. Today, most automotive
diesels are turbocharged.
1962 Oldsmobile Cutlass Jet fire
1962 Chevrolet Corvair Monza Spyder
1973 BMW 2002 Turbo
1974 Porsche 911 Turbo
1978 Saab 99
1978 Peugeot 604 turbo diesel
1978 Mercedes-Benz 300SD turbo diesel (United
States/Canada)
1979 Alfa Romeo Alfetta GTV 2000 Turbodelta
1980 Mitsubishi Lancer GT Turbo
1980 Pontiac Firebird
1980 Renault 5 Turbo
1981 Volvo 240-series Turbo
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
A turbocharger is a small radial fan pump
driven by the energy of the exhaust gases of an engine. A turbocharger consists
of a turbine and a compressor on a shared shaft. The turbine converts exhaust
heat to rotational force, which is in turn used to drive the compressor. The compressor
draws in ambient air and pumps it in to the intake manifold at increased
pressure resulting in a greater mass of air entering the cylinders on each
intake stroke.
The objective of a turbocharger is the same as
a supercharger; to improve the engine's volumetric efficiency by solving one of
its cardinal limitations. A naturally aspirated automobile engine uses only the
downward stroke of a piston to create an area of low pressure in order to draw
air into the cylinder through the intake valves. Because the pressure in the
atmosphere is no more than 1 atm (approximately 14.7 psi), there ultimately will be
a limit to the pressure difference across the intake valves and thus the amount
of airflow entering the combustion chamber.
Because the turbocharger increases the
pressure at the point where air is entering the cylinder, a greater mass of air
(oxygen) will be forced in as the inlet manifold pressure increases. The
additional air flow makes it possible to maintain the combustion chamber
pressure and fuel/air load even at high engine revolution speeds, increasing
the power and torque output of the engine. Because the pressure in the cylinder
must not go too high to avoid detonation and physical damage, the intake
pressure must be controlled by venting excess gas. The control function is
performed by a waste gate, which routes some of the exhaust flow away from the
turbine. This regulates air pressure in the intake manifold.
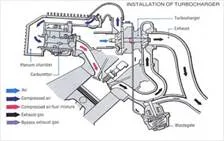
COMPONENTS OF A TURBOCHARGER
The turbocharger has four main components. The
turbine (almost always a radial turbine) and impeller/compressor wheels are
each contained within their own folded conical housing on opposite sides of the
third component, the centre housing/hub rotating assembly. The housings fitted
around the compressor impeller and turbine collect and direct the gas flow
through the wheels as they spin. The size and shape can dictate some
performance characteristics of the overall turbocharger. The turbine and
impeller wheel sizes dictate the amount of air or exhaust that can be flowed
through the system, and the relative efficiency at which they operate.
Generally, the larger the turbine wheel and compressor wheel, the larger the
flow capacity. The centre hub rotating assembly houses the shaft which connects
the compressor impeller and turbine. It also must contain a bearing system to
suspend the shaft, allowing it to rotate at very high speed with minimal
friction. Waste gates for the exhaust flow.

TURBINE WHEEL:
The Turbine Wheel is housed in the turbine
casing and is connected to a shaft that in turn rotates the compressor wheel.

COMPRESSOR WHEEL (IMPELLER)
Compressor impellers are produced using a
variant of the aluminium investment casting process. A rubber former is made to
replicate the impeller around which a casting mould is created. The rubber
former can then be extracted from the mould into which the metal is poured.
Accurate blade sections and profiles are important in achieving compressor
performance. Back face profile machining optimizes impeller stress conditions.
Boring to tight tolerance and burnishing assist balancing and fatigue
resistance. The impeller is located on the shaft assembly using a threaded nut.
WASTE GATES:
On the exhaust side, a Waste gate provides us
a means to control the boost pressure of the engine. Some commercial diesel
applications do not use a Waste gate at all. This type of system is called a
free-floating turbocharger. However, the vast majority of gasoline performance
applications require Waste gates. Waste gates provide a means to bypass exhaust
flow from the turbine wheel. Bypassing this energy (e.g. exhaust flow) reduces
the power driving the turbine wheel to match the power required for a given
boost level.

ADVANTAGES
1. More
specific power over naturally aspirated engine. This means a turbocharged
engine can achieve more power from same engine volume.
2. Better
thermal efficiency over both naturally aspirated and supercharged engine when
under full load (i.e. on boost). This is because the excess exhaust heat and
pressure, which would normally be wasted, contributes some of the work required
to compress the air.
3. Weight/Packaging.
Smaller and lighter than alternative forced induction systems and may be more
easily fitted in an engine bay.
4. Fuel
Economy. Although adding a turbocharger itself does not save fuel, it will
allow a vehicle to use a smaller engine while achieving power levels of a much
larger engine, while attaining near normal fuel economy while off
boost/cruising. This is because without boost, less fuel is used to create a
proper air/fuel ratio.
DISADVANTAGES
1. Lack
of responsiveness if an incorrectly sized turbocharger is used. If a
turbocharger that is too large is used it reduces throttle response as it
builds up boost slowly otherwise known as "lag". However, doing this
may result in more peak power.
2. Boost
threshold- A turbocharger starts producing boost only above a certain rpm due
to a lack of exhaust gas volume to overcome inertia of rest of the turbo
propeller. This results in a rapid and nonlinear rise in torque, and will
reduce the usable power band of the engine. The sudden surge of power could
overwhelm the tires and result in loss of grip, which could lead to under
steer/over steer, depending on the drive train and suspension setup of the
vehicle. Lag can be disadvantageous in racing, if throttle is applied in a
turn, power may unexpectedly increase when the turbo spools up, which can cause
excessive wheel spin.
3. Cost-
Turbocharger parts are costly to add to naturally aspirated engines. Heavily
modifying OEM turbocharger systems also require extensive upgrades that in most
cases requires most (if not all) of the original components to be replaced.
4. Complexity-
Further to cost, turbochargers require numerous additional systems if they are
not to damage an engine. Even an engine under only light boost requires a
system for properly routing (and sometimes cooling) the lubricating oil,
turbo-specific exhaust manifold, application specific downpipe, boosts
regulation. In addition inter -cooled turbo engines require additional
plumbing, while highly tuned turbocharged engines will require extensive
upgrades to their lubrication, cooling, and breathing systems; while
reinforcing internal engine and transmission parts.
TURBO LAG AND BOOST
The time required to bring the turbo up to a
speed where it can function effectively is called turbo lag. This is noticed as
a hesitation in throttle response when coming off idle. This is symptomatic of
the time taken for the exhaust system driving the turbine to come to high
pressure and for the turbine rotor to overcome its rotational inertia and reach
the speed necessary to supply boost pressure. The directly-driven compressor in
a supercharger does not suffer from this problem. Conversely on light loads or
at low RPM a turbocharger supplies less boost and the engine acts like a
naturally aspirated engine. Turbochargers start producing boost only above a
certain exhaust mass flow rate (depending on the size of the turbo). Without an
appropriate exhaust gas flow, they logically cannot force air into the engine.
The point at full throttle in which the mass flow in the exhaust is strong
enough to force air into the engine is known as the boost threshold rpm.
Engineers have, in some cases, been able to reduce the boost threshold rpm to
idle speed to allow for instant response. Both Lag and Threshold
characteristics can be acquired through the use of a compressor map and a
mathematical equation.
APPLICATIONS
Gasoline-powered cars
Today, turbocharging is commonly used by many
manufacturers of both diesel and gasoline-powered cars. Turbo charging can be
used to increase power output for a given capacity or to increase fuel
efficiency by allowing a smaller displacement engine to be used. Low pressure
turbocharging is the optimum when driving in the city, whereas high pressure
turbocharging is more for racing and driving on highways/motorways/freeways.
Diesel-powered cars
Today, many automotive diesels are
turbocharged, since the use of turbocharging improved efficiency, driveability
and performance of diesel engines, greatly increasing their popularity.
Motorcycles
The first example of a turbocharged bike is
the 1978 Kawasaki Z1R TC. Several Japanese companies produced turbocharged high
performance motorcycles in the early 1980s. Since then, few turbocharged
motorcycles have been produced.
Trucks
The first turbocharged diesel truck was
produced by Schweizer Maschinenfabrik Saurer(Swiss Machine Works Saurer) in 1938.
Aircraft
A natural use of the turbocharger is with
aircraft engines. As an aircraft climbs to higher altitudes the pressure of the
surrounding air quickly falls off. At 5,486 m (18,000 ft), the air is at half the
pressure of sea level and the airframe experiences only half the aerodynamic
drag. However, since the charge in the cylinders is being pushed in by this air
pressure, it means that the engine will normally produce only half-power at
full throttle at this altitude. Pilots would like to take advantage of the low drag
at high altitudes in order to go faster, but a naturally aspirated engine will
not produce enough power at the same altitude to do so.
Here the main aim is to effectively utilize
the non-renewable energy such as petrol and diesel. Complete combustion of the
fuels can be achieved. Power output can be increased. Wind energy can be used
for air compression. We conclude that the power as well as the efficiency is
increasing 10 to 15 % and pollution can also decrease. From the observation we
can conclude that when the full throttle valve is open at that time the engine
speed is 4000 rpm and by this the turbocharger generate 1.60 bar pressurized
air. Generally the naturally aspirated engine takes atmospheric pressurized air
to the carburettor for air fuel mixture but we can add the high density air for
the combustion so as the result the power and the complete combustion take
place so efficiency is increasing.