Two-Stroke Cycle Petrol Engine
The two-cycle carburettor type engine makes use of an airtight crankcase for partially compressing the air-fuel mixture. As the piston travels down, the mixture previously drawn into the crankcase is partially compressed. As the piston nears the bottom of the stroke, it uncovers the exhaust and intake ports. The exhaust flows out, reducing the pressure in the cylinder. When the pressure in the combustion chamber is lower than the pressure in the crankcase through the port openings to the combustion chamber, the incoming mixture is deflected upward by a baffle on the piston. As the piston moves up, it compresses the mixture above and draws into the crankcase below a new air-fuel mixture.
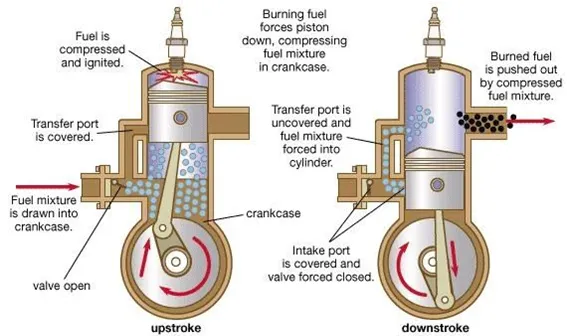
The, two-stroke cycle engine can be easily identified by the air-fuel mixture valve attached to the crankcase and the exhaust Port located at the bottom of the cylinder.