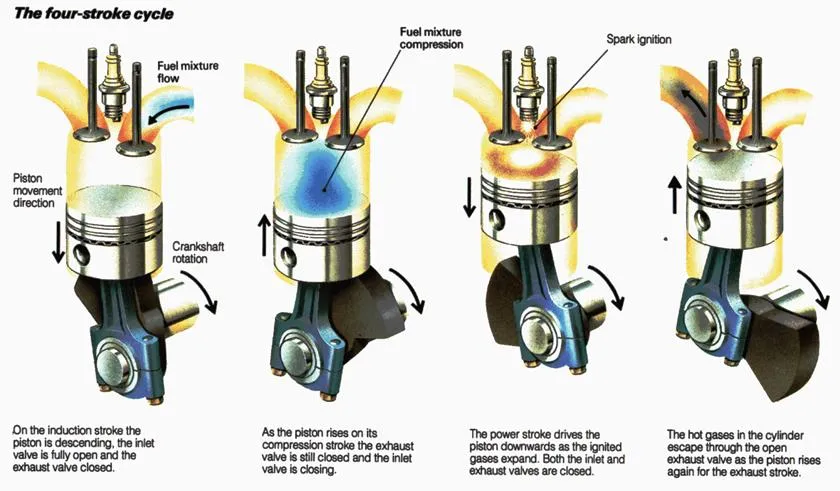
Four-Stroke Spark Ignition Engine
In this gasoline is mixed with air, broken up into a mist and partially vaporized in a carburettor . The mixture is then sucked into the cylinder. There it is compressed by the upward movement of the piston and is ignited by an electric spark. When the mixture is burned, the resulting heat causes the gases to expand. The expanding gases exert a pressure on the piston (power stroke). The exhaust gases escape in the next upward movement of the piston. The strokes are similar to those discussed under four-stroke diesel engines. The various temperatures and pressures are shown in Fig. 6. The compression ratio varies from 4:1 to 8:1 and the air-fuel mixture from 10:1 to 20:1.