Steady State Solution of DC Circuits:
Resistance in series connection:

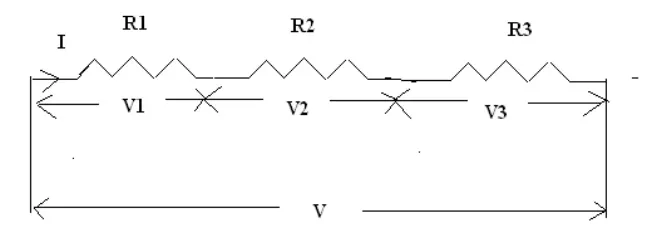
The resistors R1, R2, R3 are connected in series across the supply voltage “V”. The total current flowing through the circuit is denoted as “I”. The voltage across the resistor R1, R2 and R3 is V1, V2, and V3 respectively.
V1 = I*R1 (as per ohms law)
V2= I*R2
V3 = I*R3
V = V1+V2+V3
= IR1+IR2+IR3
= (R1+R2+R3) I IR = (R1+R2+R3) I
R = R1+R2+R3
Resistance in parallel connection:

The resistors R1, R2, R3 are connected in parallel across the supply voltage “V”. The total current flowing through the circuit is denoted as “I”. The current flowing through the resistor
R1, R2 and R3 is I1, I2, and I3 respectively.
I = V / R (as per ohms law)
I 1 = V1 / R1
I2 = V2 / R2
I3 = V3 / R3
V1 = V2 = V3 = V
From the above diagram
I = I1+I2+I3
= V1 / R1 + V2 / R2 + V3 / R3
= V / R1+ V/R2 +V/R3
I = V (1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3)
V / R = V (1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3)
1/R = 1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3