P-N junction semiconductor diode
A p-n junction diode is two-terminal or two-electrode semiconductor device, which allows the electric current in only one direction while blocks the electric current in opposite or reverse direction. If the diode is forward biased, it allows the electric current flow. On the other hand, if the diode is reverse biased, it blocks the electric current flow. P-N junction semiconductor diode is also called as p-n junction semiconductor device.
In n-type semiconductors, free electrons are the majority charge carriers whereas in p-type semiconductors, holes are the majority charge carriers. When the n-type semiconductor is joined with the p-type semiconductor, a p-n junction is formed. The p-n junction, which is formed when the p-type and n-type semiconductors are joined, is called as p-n junction diode.
The p-n junction diode is made from the semiconductor materials such as silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide. For designing the diodes, silicon is more preferred over germanium. The p-n junction diodes made from silicon semiconductors works at higher temperature when compared with the p-n junction diodes made from germanium semiconductors.
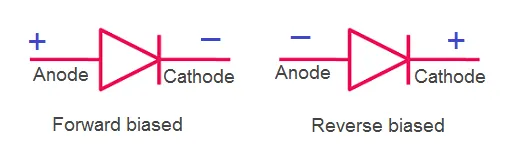
The basic symbol of p-n junction diode under forward bias and reverse bias is shown in the below figure

In the above figure, arrowhead of a diode indicates the conventional direction of electric current when the diode is forward biased (from positive terminal to the negative terminal). The holes which moves from positive terminal (anode) to the negative terminal (cathode) is the conventional direction of current.
The free electrons moving from negative terminal (cathode) to the positive terminal (anode) actually carry the electric current. However, due to the convention we have to assume that the current direction is from positive terminal to the negative terminal.
The process of applying the external voltage to a p-n junction semiconductor diode is called biasing. External voltage to the p-n junction diode is applied in any of the two methods: forward biasing or reverse biasing.
If the p-n junction diode is forward biased, it allows the electric current flow. Under forward biased condition, the p-type semiconductor is connected to the positive terminal of battery whereas; the n-type semiconductor is connected to the negative terminal of battery.
If the p-n junction diode is reverse biased, it blocks the electric current flow. Under reverse biased condition, the p-type semiconductor is connected to the negative terminal of battery whereas; the n-type semiconductor is connected to the positive terminal of battery.
Generally, terminal refers to a point or place at which any object begins or ends. For example, bus terminal or terminus is a place at which all the buses begins or ends. Similarly, in a p-n junction diode, terminal refers a point at which charge carriers begins or ends.
P-n junction diode consists of two terminals: positive and negative. At positive terminal, all the free electrons will ends and all the holes will begins whereas at negative terminal all the free electrons will begins and all the holes will ends.
In forward biased p-n junction diode (p-type connected to positive terminal and n-type connected to negative terminal), anode terminal is a positive terminal whereas cathode terminal is negative terminal.
Anode terminal is a positively charged electrode or conductor, which supplies holes to the p-n junction. In other words, anode or anode terminal or positive terminal is the source of positive charge carriers (holes), the positive charge carriers (holes) begins their journey at anode terminal and travel through the diode and ends at cathode terminal.
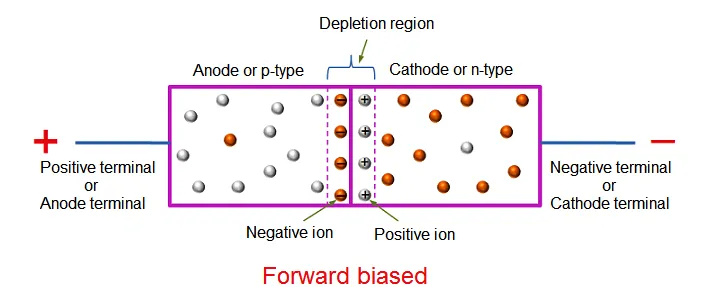
Cathode is the negatively charged electrode or conductor, which supplies free electrons to the p-n junction. In other words, cathode terminal or negative terminal is the source of free electrons, the negative charge carriers (free electrons) begins their journey at cathode terminal and travel through the diode and ends at anode terminal.
The free electrons are attracted towards the anode terminal or positive terminal whereas the holes are attracted towards the cathode terminal or negative terminal.
If the diode is reverse biased (p-type connected to negative terminal and n-type connected to positive terminal), the anode terminal becomes a negative terminal whereas the cathode terminal becomes a positive terminal.
Anode terminal or negative terminal supplies free electrons to the p-n junction. In other words, anode terminal is the source of free electrons, the free electrons begins their journey at negative or anode terminal and fills the large number of holes in the p-type semiconductor. The holes in the p-type semiconductor get attracted towards the negative terminal. The free electrons from the negative terminal cannot move towards the positive terminal because the wide depletion region at the p-n junction resists or opposes the flow of free electrons.

Cathode terminal or positive terminal supplies holes to the p-n junction. In other words, cathode terminal is the source of holes, the holes begins their journey at positive or cathode terminal and occupies the electrons position in the n-type semiconductor. The free electrons in the n-type semiconductor gets attracted towards the positive terminal. The holes from the positive terminal cannot move towards the negative terminal because the wide depletion region at the p-n junction opposes the flow of holes.
P-n junction diode is the simplest form of all the semiconductor devices. However, diodes plays a major role in many electronic devices.
The various types of diodes are as follows: