Rain Sensors
Rain sensor systems:
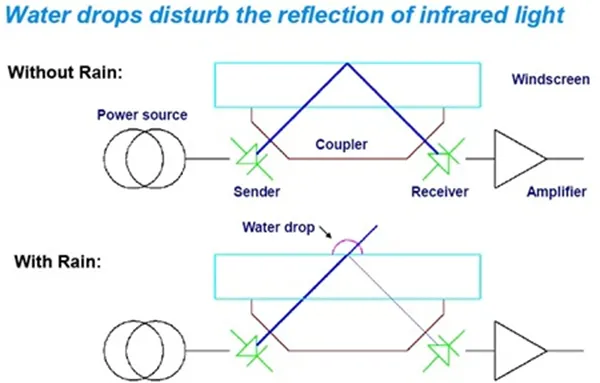
Opto electronic sensors are used in a reflective mode in rain sensor systems to detect the presence of water on the windshield so that the windshield wipers can be controlled automatically.

An LED emits light in such a way that when the windshield is dry almost the entire amount of light is reflected onto a light sensor. When the windshield is wet, the reflective behavior changes: the more water there is on the surface, the less light is reflected. In the new rain sensor, infrared light is used instead of conventional visible light. This means that the sensor can be mounted in the black area at the edge of the windshield and cannot be seen from outside.
Working Operation:
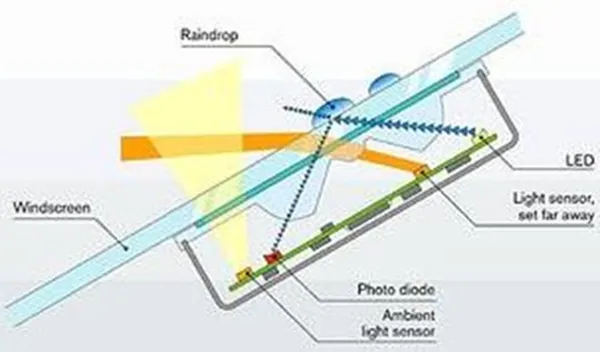
An infrared beam is reflected off the outer windshield surface back to the infrared sensor array. When moisture strikes the windshield, the system detects a reflection to its infrared beam. Advanced analogue and digital signal processing determines the intensity of rain. The sensor communicates to the wiper control module, which switches on the wiper motor and controls the wipers automatically, according to the moisture intensity detected.

Depending on the quantity of rain detected, the sensor controls the speed of the wiper system. In conjunction with electronically controlled wiper drive units, the wiping speed can be continuously adjusted in intermittent operation. In the event of splash water – as when overtaking a truck – the system switches immediately to the highest speed.
The new rain sensor offers further options. For example, it can be used to close windows and sunroofs automatically if the vehicle is parked and it starts to rain. It can even be fitted with an additional light sensor to control the headlights – at night or at the entrance to a tunnel, the lights can be switched on without any intervention by the driver.
Light Sensors:
Automatic lighting of the headlights is controlled by a passive light sensor. It measures available light using a set of photo-electric cells.

The light sensor comprises three lenses that focus the light onto three photo-electric cells. This allowed “the luminous space” surrounding the vehicle into several zones through the directivity of each basic lens cell pair.
● Lens 1: Measure total ambient light
● Lens 2: Intersect Front source of light
● Lens 3: Distinguish Road Condition (Like brighter sunny weather condition or Dark tunnel)
By comparing the information gathered by these three devices, the system computer determines the situation with which the vehicle is confronted and commands the headlights in consequence.