Introduction to Low Dropout (LDO) Linear Voltage Regulators
Linear voltage regulators are key components in any power-management system that requires a stable and ripple-free power supply. A subset of linear voltage regulators is a class of circuits known as low dropout (LDO) regulators. This paper explains the fundamentals of LDOs and introduces Vidatronic’s LDO technology which solves many of the known shortcomings of LDO circuits. LDOs are available as both stand-alone packaged devices and as intellectual property (IP) cores that can be integrated into a larger integrated circuit design. This paper deals with the fundamental principles of this class of circuits and, therefore, is applicable to both stand-alone devices and IP cores. There are several articles available regarding LDOs. While some of them are highly technical and heavy on mathematical analysis, others are generic and don't go into any detail. This paper attempts to strike the right balance to appeal to a wider audience. Several basic aspects of these circuits are discussed, with the intention of giving the reader a simple overview, rather than delving into complicated details and mathematical derivations. The motivation for this paper is to make the readers comfortable with the topic of LDOs and to prepare them for assimilating more advanced topics. Key electrical specifications are examined and contrasted against Vidatronic’s IP cores towards the end of the article, to showcase the differentiation provided by Vidatronic.
INTRODUCTION & BACKGROUND
A linear voltage regulator is a circuit that takes in a variable input voltage and provides a continuously controlled, steady, low-noise DC output voltage. Generally, linear voltage regulators require a large voltage drop between the input and the output to function correctly. This requires a relatively high-voltage input power supply and results in low power efficiency. A low dropout (LDO) linear voltage regulator is a type of linear voltage regulator circuit that works well even when the output voltage is very close to the input voltage, improving its power efficiency.
LDOs have two main functions, the first obviously being the reduction of an incoming supply voltage to the lower voltage that is needed by the load. A second function is the supply of a very low-noise voltage source, even in the presence of noise on the incoming power supply or transients in the load. In fact, this is their main advantage over switching converters, where noise isolation and emissions are major system concerns.
FUNDAMENTALS OF CIRCUIT OPERATION
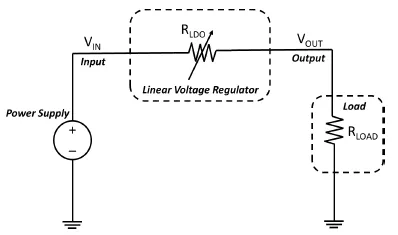
The fundamental concept of the linear voltage regulator is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Linear Voltage Regulator Fundamental Concept
In simple terms, the linear voltage regulator is an effective impedance (RLDO) that is presented to the load (RLOAD) so that the excess voltage is dropped across RLDO in order to maintain the required voltage levels at the load.
In many systems, the power supply providing the input voltage varies considerably, which, in the above implementation, would cause the output voltage to also vary by a corresponding amount. For this reason, it is necessary to add a closed-loop control system to ensure the output voltage remains constant, independent of the input line voltage. Such closed-loop feedback networks usually regulate by using a fixed voltage reference, typically provided by a bandgap reference circuit. Figure 2 depicts the closed-loop system.
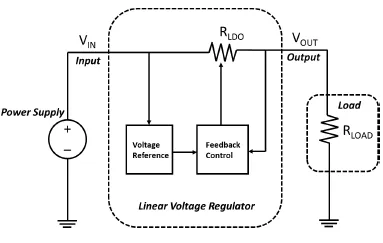
Figure 2: Simplified Linear Voltage Regulator
The linear voltage regulator output voltage (VOUT) is now independent of the input source voltage (VIN) and is directly related to the voltage reference. If this voltage reference is stable and clean, the output is generally immune to any line changes. If the control loop is fast enough, then the regulator can also maintain a steady output voltage during abrupt transient changes in load current.
When the design of the regulator is such that the minimum required voltage drop across RLDO is small (a few hundred millivolts or less), then this is known as a low dropout linear voltage regulator or simply LDO.