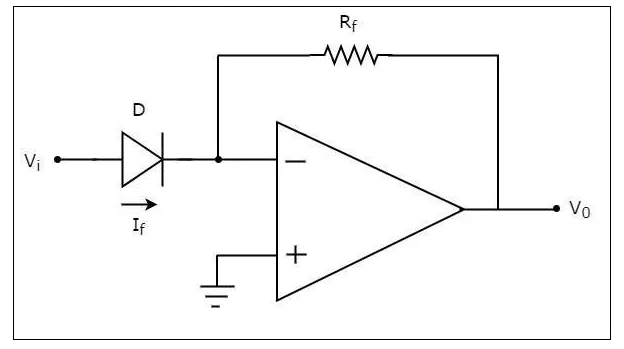
Anti-Logarithmic Amplifier
An anti-logarithmic amplifier, or an anti-log amplifier, is an electronic circuit that produces an output that is proportional to the anti-logarithm of the applied input. This section discusses about the op-amp based anti-logarithmic amplifier in detail.
An op-amp based anti-logarithmic amplifier produces a voltage at the output, which is proportional to the anti-logarithm of the voltage that is applied to the diode connected to its inverting terminal.
The circuit diagram of an op-amp based anti-logarithmic amplifier is shown in the following figure −

In the circuit shown above, the non-inverting input terminal of the op-amp is connected to ground. It means zero volts is applied to its non-inverting input terminal.
According to the virtual short concept, the voltage at the inverting input terminal of op-amp will be equal to the voltage present at its non-inverting input terminal. So, the voltage at its inverting input terminal will be zero volts.
The nodal equation at the inverting input terminal’s node is −


