Working of servomotors
Servo motors control position and speed very precisely. Now a potentiometer can sense the mechanical position of the shaft. Hence it couples with the motor shaft through gears. The current position of the shaft is converted into electrical signal by potentiometer, and is compared with the command input signal. In modern servo motors, electronic encoders or sensors sense the position of the shaft .
We give command input according to the position of shaft . If the feedback signal differs from the given input, an error signal alerts the user. We amplify this error signal and apply as the input to the motor, hence the motor rotates. And when the shaft reaches to the require position , error signal become zero , and hence the motor stays standstill holding the position.
The command input is in form of electrical pulses . As the actual input to the motor is the difference between feedback signal ( current position ) and required signal, hence speed of the motor is proportional to the difference between the current position and required position . The amount of power require by the motor is proportional to the distance it needs to travel .
Controlling of servomotors :
Usually a servomotor turns 90 degree in either direction hence maximum movement can be 180 degree . However a normal servo motor cannot rotate any further to a build in mechanical stop.
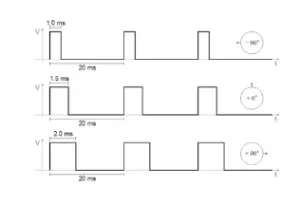
We take three wires are out of a servo : positive , ground and control wire. A servo motor is control by sending a pulse width modulated(PWM) signal through the control wire . A pulse is sent every 20 milliseconds. Width of the pulses determine the position of the shaft .
for example ,
A pulse of 1ms will move the shaft anticlockwise at -90 degree , a pulse of 1.5ms will move the shaft at the neutral position that is 0 degree and a pulse of 2ms will move shaft clockwise at +90 degree.

variable pulse width control servo motor
When we command a servo motor to move by applying pulse of appropriate width, the shaft moves to and holds the require position of the shaft. However the motor resists to change . Pulses need repetition for the motor to hold the position .