What is a Sensor?
A device that detects the changes in electrical or physical or other quantities and thereby produces an output as an acknowledgement of change in the quantity is called as a Sensor. Generally, this sensor output will be in the form of electrical or optical signal.
The most frequently used different types of sensors are classified based on the quantities such as Electric current or Potential or Magnetic or Radio sensors, Humidity sensor, Fluid velocity or Flow sensors, Pressure sensors, Thermal or Heat or Temperature sensors, Proximity sensors, Optical sensors, Position sensors, Chemical sensor, Environment sensor, Magnetic switch sensor , etc.
Typical applications of different types of sensors such as application of Speed sensor for synchronizing the speed of multiple motors, Temperature sensor application for industrial temperature control, application of the PIR sensor for automatic-door-opening system, Ultrasonic sensor application for distance measurement, etc., are discussed below with their block diagrams.
Sensors used for detecting speed of an object or vehicle is called as Speed sensor. There are different types of sensors to detect the speed such as Wheel speed sensors, speedometers, LIDAR, ground speed radar, pitometer logs, doppler radar, air speed indicators, pitot tubes and so on.

Sensors used for detecting speed of an object or vehicle is called as Speed sensor. There are different types of sensors to detect the speed such as Wheel speed sensors, speedometers, LIDAR, ground speed radar, pitometer logs, doppler radar, air speed indicators, pitot tubes and so on.
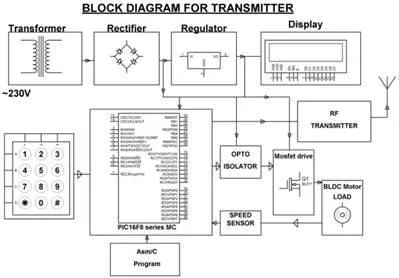
PIC microcontroller based project for speed synchronization of multiple motors in industries using wireless technology is a typical application of the speed sensor. One of the multiple motors in the industry is considered as a main motor which act as transmitter and remaining motors acting as receivers, will follow the speed of the main motor. The main motor and receiver motors used in this project are BLDC motors that are controlled using PWM control with the radio frequency wireless communication mode.

Reference RPM is given to each motor shaft which has an IR sensor mounted and a closed loop is obtained by feeding this output to controller in the circuit. Full speed will be displayed on display unit and required speed of all motors can be obtained by entering the desired percentage using the keypad. This entered percentage is matched with running RPM by maintaining appropriate DC power to motor with automatic adjustment of pulse width output of microcontroller.
Thus, by varying speed of transmitting motor, we can change the speed of all motors using this technology