Choice of automated equipment
Architecture implementation
We propose to help the customer by addressing their problem to guide them and optimise their choice of architecture and the products and services it will include. This process starts by ascertaining the customer’s needs and structuring questions as we shall describe.
To make it easier to choose, Schneider Electric has optimised a number of variants based on the most common architectures.
The first involves compact applications where the automated devices are grouped into an «all-in-one panel».
The second relates to procedure-distributed applications. The automated devices are divided up into several panels known as «distributed peripherals».
The other two (All in One Device and Collaborative Control) are not left out, but are presented differently. The «all-in-one device» structure is comparable to a single device and is treated as such. The «collaborative control» structure mainly involves data exchange between devices and is described in the section on links and exchanges. Its details are in the sections on automated devices and software.
Choices offered by Schneider Electric
Both architecture concepts above can be implemented in many ways. To make it easier for the customer to choose, Schneider Electric has opted for a total of 10 possible implementations to offer optimal combinations.
To prevent any confusion between the architecture concepts described above and the practical solutions Schneider Electric proposes, the latter will be referred to as preferred implementations.

Choice of a preferred implementation
The solution approach to these implementations, which includes all the customer’s requirements, has many advantages:
- simplified choice of automation systems,
- peace of mind and confidence for the user because the devices are interoperable and performance levels are guaranteed,
- once the implementation is chosen, the customer will have an adequately precise framework, alongside the catalogue and specific guides, to select the requisite automated functions and devices,
- commissioning is facilitated by the work completed upstream.
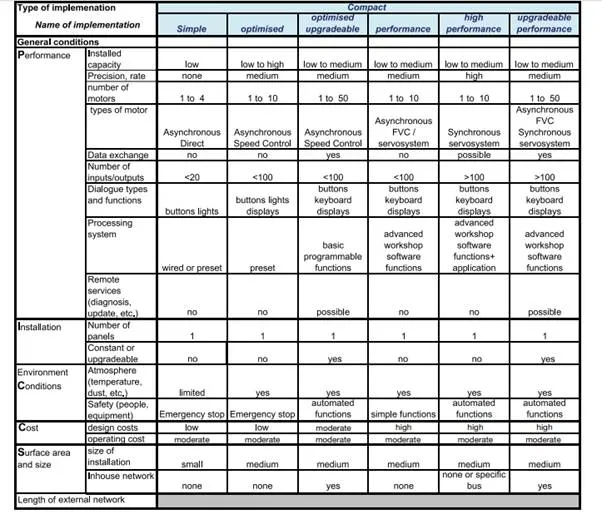
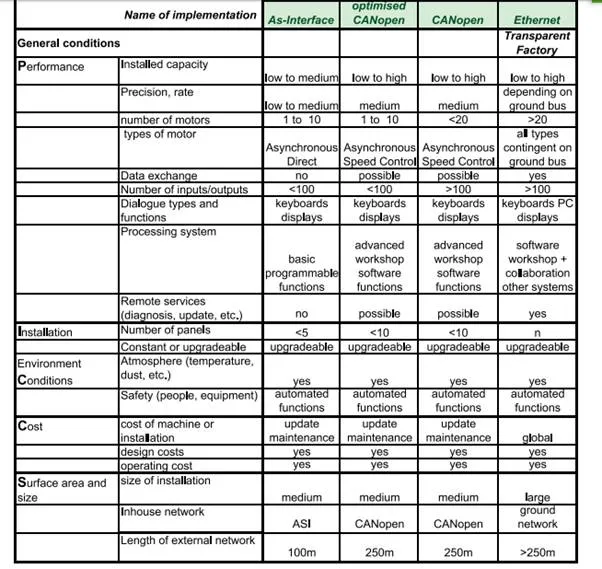
To assist customers choice, Schneider Electric has drawn up a complete guide with questions divided into four themes given the mnemonic of PICCS (Performance, Installation, Constraints, Cost, Size). An example is given below. For all the implementations available, please refer to the catalogues. Here we are just illustrating the approach with examples


We shall take three different applications and ascertain the most suitable architecture(s) for each of them.