What is Unit Testing?
UNIT Testing is defined as a type of software testing where individual units/ components of a software are tested. Unit Testing of software applications is done during the development (coding) of an application. The objective of Unit Testing is to isolate a section of code and verify its correctness. In procedural programming, a unit may be an individual function or procedure. Unit Testing is usually performed by the developer.
In SDLC, STLC, V Model, Unit testing is first level of testing done before integration testing. Unit testing is a WhiteBox testing technique that is usually performed by the developer. Though, in a practical world due to time crunch or reluctance of developers to tests, QA engineers also do unit testing.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
- What is Unit Testing?
- Why Unit Testing?
- How to do Unit Testing
- Unit Testing Techniques
- Unit Testing Tools
- Test Driven Development (TDD) & Unit Testing
- Unit Testing Myth
- Unit Testing Advantage
- Unit Testing Disadvantages
- Unit Testing Best Practices
Why Unit Testing?
Sometimes software developers attempt to save time by doing minimal unit testing. This is a myth because skipping on unit testing leads to higher Defect fixing costs during System Testing, Integration Testing and even Beta Testing after the application is completed. Proper unit testing done during the development stage saves both time and money in the end. Here, are key reasons to perform unit testing.
- Unit Tests fix bug early in development cycle and save costs.
- It helps understand the developers the code base and enable them to make changes quickly
- Good unit tests serve as project documentation
- Unit tests help with code re-use. Migrate both your code andyour tests to your new project. Tweak the code till the tests run again.
How to do Unit Testing
Unit Testing is of two types
Unit testing is commonly automated but may still be performed manually. Software Engineering does not favor one over the other but automation is preferred. A manual approach to unit testing may employ a step-by-step instructional document.
Under the automated approach-
- A developer writes a section of code in the application just to test the function. They would later comment out and finally remove the test code when the application is deployed.
- A developer could also isolate the function to test it more rigorously. This is a more thorough unit testing practice that involves copy and paste of code to its own testing environment than its natural environment. Isolating the code helps in revealing unnecessary dependencies between the code being tested and other units or data spaces in the product. These dependencies can then be eliminated.
- A coder generally uses a UnitTest Framework to develop automated test cases. Using an automation framework, the developer codes criteria into the test to verify the correctness of the code. During execution of the test cases, the framework logs failing test cases. Many frameworks will also automatically flag and report, in summary, these failed test cases. Depending on the severity of a failure, the framework may halt subsequent testing.
- The workflow of Unit Testing is 1) Create Test Cases 2) Review/Rework 3) Baseline 4) Execute Test Cases.
Unit Testing Techniques
Code coverage techniques used in united testing are listed below:
- Statement Coverage
- Decision Coverage
- Branch Coverage
- Condition Coverage
- Finite State Machine Coverage
Unit Testing Example: Mock Objects
Unit testing relies on mock objects being created to test sections of code that are not yet part of a complete application. Mock objects fill in for the missing parts of the program.
For example, you might have a function that needs variables or objects that are not created yet. In unit testing, those will be accounted for in the form of mock objects created solely for the purpose of the unit testing done on that section of code.
Unit Testing Tools
There are several automated tools available to assist with unit testing. We will provide a few examples below:
- Jtest: Parasoft Jtest is an IDE plugin that leverages open-source frameworks (Junit, Mockito, PowerMock, and Spring) with guided and easy one-click actions for creating, scaling, and maintaining unit tests. By automating these time-consuming aspects of unit testing, it frees the developer to focus on business logic and create more meaningful test suites.
- Junit: Junit is a free to use testing tool used for Java programming language. It provides assertions to identify test method. This tool test data first and then inserted in the piece of code.
- NUnit: NUnit is widely used unit-testing framework use for all .net languages. It is an open source tool which allows writing scripts manually. It supports data-driven tests which can run in parallel.
- JMockit: JMockit is open source Unit testing tool. It is a code coverage tool with line and path metrics. It allows mocking API with recording and verification syntax. This tool offers Line coverage, Path Coverage, and Data Coverage.
- EMMA: EMMA is an open-source toolkit for analyzing and reporting code written in Java language. Emma support coverage types like method, line, basic block. It is Java-based so it is without external library dependencies and can access the source code.
- PHPUnit: PHPUnit is a unit testing tool for PHP programmer. It takes small portions of code which is called units and test each of them separately. The tool also allows developers to use pre-define assertion methods to assert that a system behave in a certain manner.
Those are just a few of the available unit testing tools. There are lots more, especially for C languages and Java, but you are sure to find a unit testing tool for your programming needs regardless of the language you use.
Test Driven Development (TDD) & Unit Testing
Unit testing in TDD involves an extensive use of testing frameworks. A unit test framework is used in order to create automated unit tests. Unit testing frameworks are not unique to TDD, but they are essential to it. Below we look at some of what TDD brings to the world of unit testing:
- Tests are written before the code
- Rely heavily on testing frameworks
- All classes in the applications are tested
- Quick and easy integration is made possible
Myths by their very nature are false assumptions. These assumptions lead to a vicious cycle as follows -
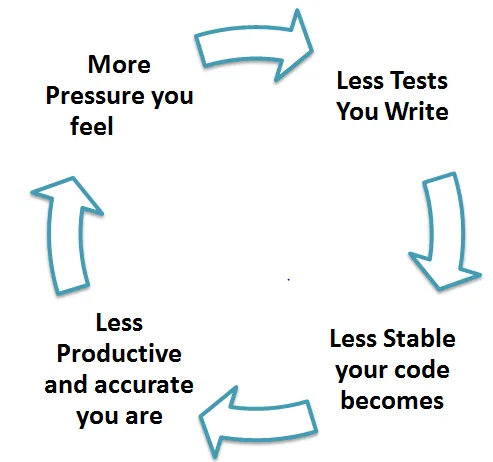
Truth is Unit testing increase the speed of development.
Programmers think that Integration Testing will catch all errors and do not execute the unit test. Once units are integrated, very simple errors which could have very easily found and fixed in unit tested take a very long time to be traced and fixed.
Unit Testing Advantage
- Developers looking to learn what functionality is provided by a unit and how to use it can look at the unit tests to gain a basic understanding of the unit API.
- Unit testing allows the programmer to refactor code at a later date, and make sure the module still works correctly (i.e. Regression testing). The procedure is to write test cases for all functions and methods so that whenever a change causes a fault, it can be quickly identified and fixed.
- Due to the modular nature of the unit testing, we can test parts of the project without waiting for others to be completed.
Unit Testing Disadvantages
- Unit testing can't be expected to catch every error in a program. It is not possible to evaluate all execution paths even in the most trivial programs
- Unit testing by its very nature focuses on a unit of code. Hence it can't catch integration errors or broad system level errors.
It's recommended unit testing be used in conjunction with other testing activities.
Unit Testing Best Practices
- Unit Test cases should be independent. In case of any enhancements or change in requirements, unit test cases should not be affected.
- Test only one code at a time.
- Follow clear and consistent naming conventions for your unit tests
- In case of a change in code in any module, ensure there is a corresponding unit Test Case for the module, and the module passes the tests before changing the implementation
- Bugs identified during unit testing must be fixed before proceeding to the next phase in SDLC
- Adopt a "test as your code" approach. The more code you write without testing, the more paths you have to check for errors.

Summary
As you can see, there can be a lot involved in unit testing. It can be complex or rather simple depending on the application being tested and the testing strategies, tools and philosophies used. Unit testing is always necessary on some level. That is a certainty.



