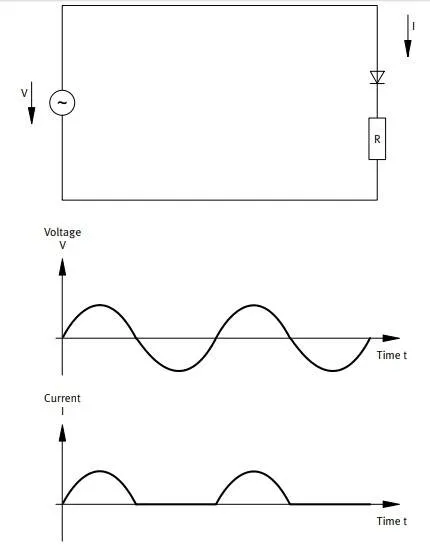
How a diode works ?
Diodes are electrical (semiconductor) components whose resistance differs depending on the direction in which the electrical current is flowing:
• When the diode is switched in the free-flow direction its resistance is very low, which means the electrical current can flow almost unimpeded.
• When it is switched in the blocked direction its resistance is extremely high, which means no current can flow.
When a diode is integrated in an AC circuit, the current can only flow in one direction. The electrical current is rectified (see Figure 3.6). A diode's effect on the electrical current can be compared to the effect of a bicycle valve that allows air to enter a tyre but prevents it from escaping again.
