Pressure
1 Pa corresponds to the pressure exerted by a vertical force of 1 N on an area of 1 m2 .
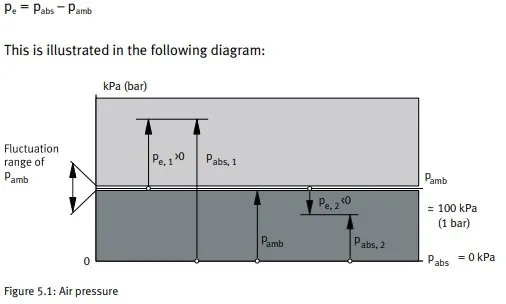
The pressure on the earth's surface is referred to as atmospheric pressure (pamb). This pressure is also called reference pressure. The range above this pressure is called the excess pressure range (pe > 0), while the range below is called the vacuum range (pe < 0). The atmospheric pressure differential pe is calculated according to the formula:

Atmospheric pressure is not constant; its value changes depending on the geographical location and the weather. Absolute pressure pabs is the value referred to as zero pressure (vacuum). It is equal to the sum of the atmospheric pressure and excess pressure or vacuum. The pressure gauges used most frequently in practice are those that display only the excess pressure pe. The absolute pressure value pabs is approximately 100 kPa (1 bar) higher.
It is usual in pneumatics to refer all specifications relating to air quantities to the so-called normal condition. The normal condition to DIN 1343 is the condition of a solid, liquid or gaseous material defined by means of standard temperature and standard pressure.
• Standard temperature Tn = 273.15 K, tn = 0 °C
• Standard pressure pn = 101325 Pa = 1.01325 bar