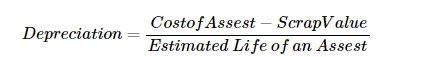
Depreciation, Reserves and Provision
Value of depreciation reduces the value of assets on residual basis and also the current year profits.
Depreciation indicates the reduction in value of any fixed assets. Reduction in value of assets depends on the life of assets. Life of assets depends upon the usage of assets.
There are many deciding factors which ascertain the life of assets; in case of a building, the deciding factor is time, the deciding factor for leased assets is the lease period, the deciding factor for plant and machinery is both production and time. There may be many factors but ascertainment of life should be based on some reasonable basis.
Following are the main causes of depreciation −
One of the main reasons of depreciation is normal wear & tears, it depends upon the usage of machinery. More the machinery is in use, more will be the wear and tear. Wear and tear of a machine in use for one shift will be less than with a machine being used in two shifts.
Some assets may lose their value due to consumption, for example, mines, quarries, oil walls and forest stands. Due to continuous extraction a stage will come where all above are completely exhausted
New technology or invention may bring down the value of old asset and outdated technology become cheaper. For example, television became obsolete with the introduction of new LED Television, the users are discarded old televisions although they are in good condition.
Value of assets may reduce over a passage of time. For example, a patent becomes useless after expiry of the period of patent.
· To ascertain the true profit of the year, it is desirable to charge depreciation.
· To ascertain true value of assets, depreciation should be charged and without correct value of assets, true financial position of the company cannot be ascertained.
· Instead of withdrawal of overstated profit, it is desirable to make provisions to buy new asset and replace the old asset. Accumulated value of depreciation provides additional working capital.
· Depreciation help us to ascertain uniform profit in each accounting year.
· Depreciation is also useful to gain advantage o tax benefits.
The important factors related to the depreciation chargeable are as follows −
Following are the methods of depreciation −
Depreciation may be charged by applying any of the above methods. We will discuss a few important methods −
Under this method, fixed amount of depreciation is charged every year. The formula to determine the amount of depreciation is as follows;
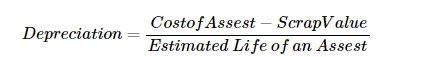
It is also called the Diminishing Balance or the Reducing Balance Method. Under this method, a fixed percentage of depreciation is charged on written down value of asset. Written down value of asset means (Cost of asset – depreciation).
The Auditor cannot be held responsible for estimating the working life of an asset; it is the job of an expert valuer.
· A company can adopt different methods for different type of assets provided that the methods are adopted consistently over the years.
· If a company opts to choose new depreciation methods, then depreciation should be recalculated applying new methods from the date on which the asset is put to use for the first time. The difference of amount of depreciation as charged with old rate and the amount calculated from new rate should be debited to profit and loss account in case of loss and difference should be credited to general reserve in case of profit.
· According to Schedule II of the Companies Act, if asset is sold or discarded during the year, depreciation will be charged on pro-rata basis up to date of sale or discard. Similarly, depreciation will be charged on pro-rata basis, in case of addition to fixed asset.
· Account must disclose method of depreciation.
· Depreciation must be according to provisions of Companies Act and Income Tax Act.
· If depreciation is charged more than prescribed rate, Auditor should examine whether it is based on some professional and technical advice.
· Depreciation should be charged on revalued amount, if there is revaluation of assets.