When different waves collide (e.g. sound from different sources) they interfere with each other. This is called, unsurprisingly, wave interference.
Phasing
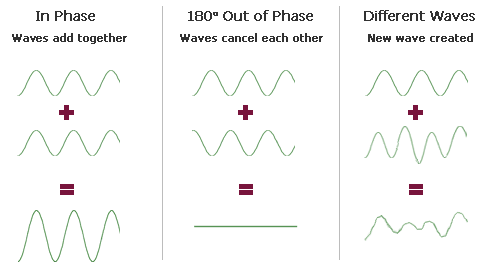
The following table illustrates how sound waves (or any other waves) interfere with each other depending on their phase relationship:

· Sound waves which are exactly in phase add together to produce a stronger wave.
· Sound waves which are exactly inverted, or 180 degrees out of phase, cancel each other out and produce silence. This is how many noise-cancellation devices work.
· Sound waves which have varying phase relationships produce differing sound effects.
Here are some examples of waves with various properties. These animations have kindly been supplied by Alexander Churenkov.
Wave Movement | Wavelength | Amplitude | Phase | Attenuation |
| 50 | 10 | 0 | 0.002 |
| 150 | 10 | 0 | 0.002 |
| 50 | 20 | 0 | 0.002 |
| 50 | 20 | 0.5 | 0.002 |
| 50 | 40 | 0 | 0.007 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|