What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a system that can learn from example through self-improvement and without being explicitly coded by programmer. The breakthrough comes with the idea that a machine can singularly learn from the data (i.e., example) to produce accurate results.
Machine learning combines data with statistical tools to predict an output. This output is then used by corporate to makes actionable insights. Machine learning is closely related to data mining and Bayesian predictive modeling. The machine receives data as input, use an algorithm to formulate answers.
A typical machine learning tasks are to provide a recommendation. For those who have a Netflix account, all recommendations of movies or series are based on the user's historical data. Tech companies are using unsupervised learning to improve the user experience with personalizing recommendation.
Machine learning is also used for a variety of task like fraud detection, predictive maintenance, portfolio optimization, automatize task and so on.
How does Machine learning work?
Machine learning is the brain where all the learning takes place. The way the machine learns is similar to the human being. Humans learn from experience. The more we know, the more easily we can predict. By analogy, when we face an unknown situation, the likelihood of success is lower than the known situation. Machines are trained the same. To make an accurate prediction, the machine sees an example. When we give the machine a similar example, it can figure out the outcome. However, like a human, if its feed a previously unseen example, the machine has difficulties to predict.
The core objective of machine learning is the learning and inference. First of all, the machine learns through the discovery of patterns. This discovery is made thanks to the data. One crucial part of the data scientist is to choose carefully which data to provide to the machine. The list of attributes used to solve a problem is called a feature vector. You can think of a feature vector as a subset of data that is used to tackle a problem.
The machine uses some fancy algorithms to simplify the reality and transform this discovery into a model. Therefore, the learning stage is used to describe the data and summarize it into a model.
For instance, the machine is trying to understand the relationship between the wage of an individual and the likelihood to go to a fancy restaurant. It turns out the machine finds a positive relationship between wage and going to a high-end restaurant.
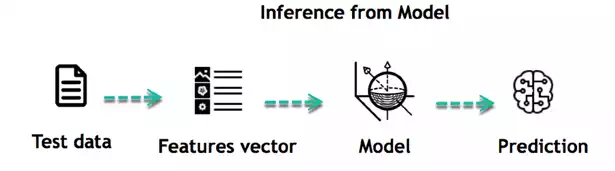
Inferring
When the model is built, it is possible to test how powerful it is on never-seen-before data. The new data are transformed into a features vector, go through the model and give a prediction. This is all the beautiful part of machine learning. There is no need to update the rules or train again the model. You can use the model previously trained to make inference on new data.
The life of Machine Learning programs is straightforward and can be summarized in the following points:
- Define a question
- Collect data
- Visualize data
- Train algorithm
- Test the Algorithm
- Collect feedback
- Refine the algorithm
- Loop 4-7 until the results are satisfying
- Use the model to make a prediction
Once the algorithm gets good at drawing the right conclusions, it applies that knowledge to new sets of data.