This can be regarded as a more general approach to representing uncertainty than the Bayesian approach.
Bayesian methods are sometimes inappropriate:
Let A represent the proposition Demi Moore is attractive.
Then the
axioms of probability insist that ![]()
Now suppose that Andrew does not even know who Demi Moore is.
Then
- We cannot say that Andrew believes the proposition if he has no idea what it means.
- Also, It is not fair to say that he disbelieves the proposition.
- It
would therefore be meaningful to denote Andrew's belief of B(A)
and
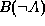 as
both being 0.
as
both being 0. - Certainty factors do not allow this.
Dempster-Shafer Calculus
The basic idea in representing uncertainty in this model is:
- Set up a confidence interval -- an interval of probabilities within which the true probability lies with a certain confidence -- based on the Belief B and plausibility PL provided by some evidence E for a proposition P.
- The belief brings together all the evidence that would lead us to believe in P with some certainty.
- The plausibility brings together the evidence that is compatible with P and is not inconsistent with it.
- This method allows for further additions to the set of knowledge and does not assume disjoint outcomes.
If ![]() is the set of possible outcomes, then a mass probability, M,
is defined for each member of the set
is the set of possible outcomes, then a mass probability, M,
is defined for each member of the set ![]() and takes
values in the range [0,1].
and takes
values in the range [0,1].
The Null set, ![]() , is also a member
of
, is also a member
of ![]() .
.
NOTE: This deals wit set theory terminology that will be dealt with in a tutorial shortly. Also see exercises to get experience of problem solving in this important subject matter.
M is a probability
density function defined not just for ![]() but
for em all subsets.
but
for em all subsets.
So if ![]() is the set { Flu
(F), Cold (C), Pneumonia (P) } then
is the set { Flu
(F), Cold (C), Pneumonia (P) } then ![]() is the set
{
is the set
{ ![]() , {F}, {C}, {P}, {F, C}, {F, P},
{C, P}, {F, C, P} }
, {F}, {C}, {P}, {F, C}, {F, P},
{C, P}, {F, C, P} }
- The
confidence interval is then defined as [B(E),PL(E)]
where

where i.e. all the
evidence that makes us believe in the correctness of P,
and
i.e. all the
evidence that makes us believe in the correctness of P,
and

where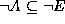 i.e. all the
evidence that contradicts P.
i.e. all the
evidence that contradicts P.
Combining beliefs
- We have the ability to assign M to a set of hypotheses.
- To combine multiple sources of evidence to a single (or multiple) hypothesis do the following:
- Suppose
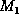 and
and 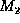 are two
belief functions.
are two
belief functions. - Let X be
the set set of subsets of
 to
which
to
which 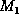 assigns
a nonzero value and letY be a similar set for
assigns
a nonzero value and letY be a similar set for 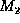
- Then
to get a new belief function
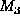 from
the combination of beliefs in
from
the combination of beliefs in 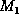 and
and 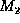 we do:
we do:
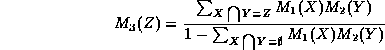
whenever ![]() .
.
NOTE: We define ![]() to be 0 so
that the orthogonal sum remains a basic probability assignment.
to be 0 so
that the orthogonal sum remains a basic probability assignment.