Declaring components
The primary task of the manifest is to inform the system about the app's components. For example, a manifest file can declare an activity as follows:
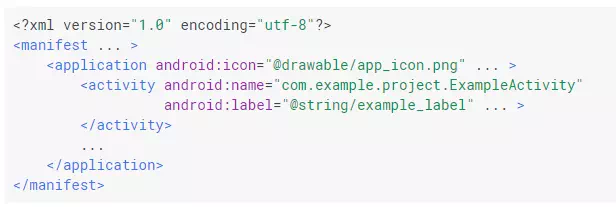
In the <application> element, the android:icon attribute points to resources for an icon that identifies the app.
In the <activity> element, the android:name attribute specifies the fully qualified class name of the Activitysubclass and the android:label attribute specifies a string to use as the user-visible label for the activity.
You must declare all app components using the following elements:
- <activity> elements for activities.
- <service> elements for services.
- <receiver> elements for broadcast receivers.
- <provider> elements for content providers.
Activities, services, and content providers that you include in your source but do not declare in the manifest are not visible to the system and, consequently, can never run. However, broadcast receivers can be either declared in the manifest or created dynamically in code as BroadcastReceiver objects and registered with the system by calling registerReceiver().
For more about how to structure the manifest file for your app, see The AndroidManifest.xml File documentation.