Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is the study of forces and the resulting motion of objects through the air.
Studying the motion of air around an object allows us to measure the forces of lift, which allows an aircraft to overcome gravity, and drag, which is the resistance an aircraft “feels” as it moves through the air. Everything moving through the air (including airplanes, rockets, and birds) is affected by aerodynamics.
In this section, we will explore how lift and drag work at both subsonic speeds—slower than the speed of sound—and, later, at supersonic speeds—faster than the speed of sound.
Aerodynamics is the way air moves around things. The rules of aerodynamics explain how an airplane is able to fly. Anything that moves through air reacts to aerodynamics. A rocket blasting off the launch pad and a kite in the sky react to aerodynamics. Aerodynamics even acts on cars, since air flows around cars.
What Are the Four Forces of Flight?
The four forces of flight are lift, weight, thrust and drag. These forces make
an object move up and down, and faster or slower. How much of each force there
is changes how the object moves through the air.

What Is Weight?
Everything on Earth has weight. This force comes
from gravity pulling down on objects. To fly, an aircraft needs something to
push it in the opposite direction from gravity. The weight of an object
controls how strong the push has to be. A kite needs a lot less upward push
than a jumbo jet does.
What Is Lift?
Lift is the push that lets something move up. It
is the force that is the opposite of weight. Everything that flies must have
lift. For an aircraft to move upward, it must have more lift than weight. A hot
air balloon has lift because the hot air inside is lighter than the air around
it. Hot air rises and carries the balloon with it. A helicopter's lift comes
from the rotor blades at the top of the helicopter. Their motion through the
air moves the helicopter upward. Lift for an airplane comes from its wings.
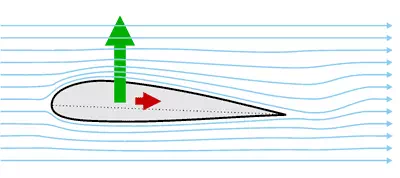
How Do an Airplane's Wings Provide Lift?
The shape of an airplane's wings is what makes
it able to fly. Airplanes' wings are curved on top and flatter on the bottom.
That shape makes air flow over the top faster than under the bottom. So, less
air pressure is on top of the wing. This condition makes the wing, and the
airplane it's attached to, move up. Using curves to change air pressure is a
trick used on many aircraft. Helicopter rotor blades use this trick. Lift for
kites also comes from a curved shape. Even sailboats use this concept. A boat's
sail is like a wing. That's what makes the sailboat move.
What Is Drag?
Drag is a force that tries to slow something
down. It makes it hard for an object to move. It is harder to walk or run
through water than through air. That is because water causes more drag than
air. The shape of an object also changes the amount of drag. Most round
surfaces have less drag than flat ones. Narrow surfaces usually have less drag
than wide ones. The more air that hits a surface, the more drag it makes.
What Is Thrust?
Thrust is the force that is the opposite of
drag. Thrust is the push that moves something forward. For an aircraft to keep
moving forward, it must have more thrust than drag. A small airplane might get its
thrust from a propeller. A larger airplane might get its thrust from jet
engines. A glider does not have thrust. It can only fly until the drag causes
it to slow down and land.
