Root Zone Waste Water Treatment
The sight of filthy sewage flowing unrestricted into our rivers is not new. Our government spends humungous amount of public funds for treating sewage water before it is discharged into the rivers. However, the sad state of our rivers indicates that a lot is left to be desired. High maintenance cost is the main deterrent for people from having a sewage treatmentplant installed in their industry or residential area. So, they completely depend on state managed and operated Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs), which often malfunction due to overload. While every large city in India has large-scale conventional STPs, they usually fall into disuse due to their high operating costs, equipment corrosion and lack of skilled operating personnel. If sewage is treated at each industry and residential colony, a major portion of the problem can be mitigated.
Approximately 70% of domestic water is released as wastewater, most of which can be recovered if it is properly treated. Hence, wastewater should be seen as a resource rather than waste. Wastewater can be mainly classified into two categories:
· Grey water – wastewater generated from kitchens, laundry, bathrooms, etc.
· Black water – wastewater from toilets containing faecal matter and urine, which is also called as “sewage”
Both grey water and black water can be suitably treated by root zone wastewater treatment and reused for non-potable applications such as toilet flushing and kitchen gardening. Among the many types of STPs, Root Zone Wastewater Treatment (RZWT) is the most innovative and eco-friendly system. The Root Zone Waste Water Treatment system is a low cost, virtually zero energy and maintenance-free plant. What’s more, it is pretty good looking too!!!
What exactly is Root Zone Wastewater Treatment?
‘Root Zone’ is a scientific term used to cover all the biological activity among different types of microbes, the roots of plants, water soil and the sun. It consists planted filter-beds containing gravel, sand and soil. The RZWT system utilises nature’s way of biologically processing domestic & industrial effluents. This effective technology called Decentralised Wastewater Systems (DEWATS) was developed in 1970s in Germany and has been successfully implemented in different countries mainly in Europe and America.

The root zone waste water treatment system makes use of biological and physical-treatment processes to remove pollutants from wastewater. Due to its natural process, there is no need to add any input such as chemicals, mechanical pumps or external energy. This reduces both the maintenance and energy costs.
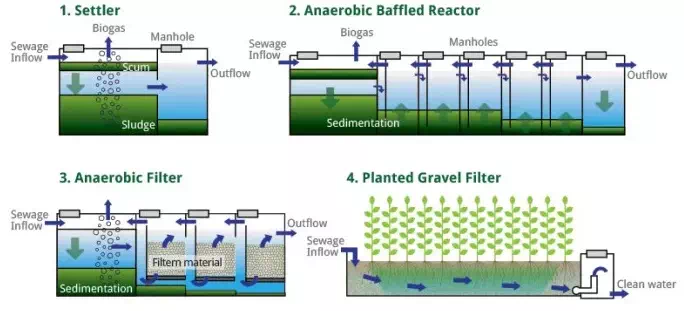
To accomplish this, the root zone wastewater treatment undertakes the following steps:
1. Pre-treatment done in a Settler – a device that separates the liquid from the solid
2. First treatment takes place in a Anaerobic Baffled Reactor – a device with several identical chambers through which the effluent moves from top to bottom.
3. Second treatment happens in an Anaerobic Filter – a device filled with a filter material (cinder), through which the effluent moves from top to bottom.
4. Third treatment takes place in a Planted Gravel Filter – a structure filled with gravel material and planted with water-resistant reed plants, which provide oxygen to the passing effluent.
1. Settler |
2. Anaerobic Baffled Reactor |
3. Anaerobic Filter | 4.
4. Planted Gravel Filter
The Root Zone Waste Water Treatment system takes into account the natural slope of the ground, so that water flows from one device to another without any external energy input such as motor pump. Once the reed plants create an established stand, usually after the first growing season, the reed bed requires little or no maintenance. The plant foliage will soon blend naturally into the landscape, ever changing with the seasons and creating a pleasing sight as well!
|
Conventional Water Treatment Plant |
Root Zone Treatment Plant |
|
A lot of sewage aeration tanks powered with mechanical energy do not work because of power cuts, technical problems and poor maintenance |
By its treatment and construction features DEWATS is designed to limit operation and maintenance requirements and in the same to ensure high treatment standards even for shock loads |
|
Requires lot of external energy |
Minimal need for external energy |
|
Pumps needed |
Using gravity instead of pumps, avoiding valves |
|
Regular maintenance required |
Zero maintenance |
|
High operating costs |
Low operating costs |

In India, this project was first executed by Bremen Overseas Research and Development Association (BORDA) in the Auroville global community. Since the last 15 years, Auroville located in South India near Pondicherry has been experimenting with such natural wastewater recycling systems. Auroville has now become a pioneer in the Root Zone Wastewater Treatment System and has enabled many such plants across India. Another such treatment plant has now been implemented in Aravind Eye Hospital, Pondicherry by Ascenso Management & Consulting Services.