Crystal Method in Agile
When in 1991, IBM asked Alistair Cockburn to develop the methodology for Object-oriented-project; he knew it’s going to be challenging. After extensive research, he concluded that all successful teams shared the same pattern and techniques without using any specific Project methodology. Consequently, he used his findings and constructed a family of methodologies and named it Crystal.
Crystal methodology is one of the most lightweight and flexible approaches to develop software. Moreover, it is made up of several agile processes, including Clear, Crystal Yellow, Crystal Orange, and other uniquely characterized methods.
To conclude, the Crystal family focuses on the realization that each project has unique characteristics. Hence, the policies and practices must be custom-tailored to accommodate these features.
The Crystal method has several essentials, which are known as Crystal properties:
Teamwork: First is teamwork which concentrates on giving team members tasks and additionally, encourages them to do tasks as a team and not as individuals.
Communication: Second is Communication. It is the most critical aspect of any project. Proper communication through email or face-to-face is required between Customer and Developers. Additionally, it is vital within the teams as well.
Simplicity: Third property focuses on the fact that Product Design, Requirement Document, and other documentation have to be understandable and straightforward. It will enable everyone to understand and work more efficiently.
Reflection: Next property is all about achieving three primary aspects of Reflection, that is:
Responding and reporting correctly: Firstly, everyone related to the project should respond as and when required. Additionally, they should provide all the updates on time to make it easy for others to understand the progress.
Reasoning: Secondly, this means providing a valid reason for every action. Developers and testers should have the right logic for each of their efforts to not let their activity consider a waste.
Reconstruction as and when needed: Finally, Tester and Developers should be well aware of all the stages they performed so that it is easy to reverse and reconstruct coding.
Frequent adjustments: The team should be able to make the adjustments as per the situation and the required changes.
Improve processes: Improvement is a continuous process. They can be improved basis customer feedback, internal feedback, from meeting output, after the root cause analysis of any bug.
In the same vein as other Agile methods, Crystal Methodology also promotes on time and frequent working software delivery. It inspires high user participation, adaptability, and exclusions of distractions and any waste.
The basis of the Crystal Method is on two critical assumptions:
v First, the team can make itself more efficient by streamlining their work and the project.
v Second, every project is different from others and requires some specific methods and strategies.
According to Alistair, every project is a game, and we need to make a strategy to win the game. He said we should include everyone, allow them to interact and welcome everyone’s idea while planning for a project. According to him, we should not focus on what we made; we should focus on what the customer wants us to make?
Crystal methods focus on:-
Ø People involved
Ø Interaction between the teams
Ø Community
Ø Skills of people involved
Ø Their Talents
Ø Communication between all the teams
The Crystal family:
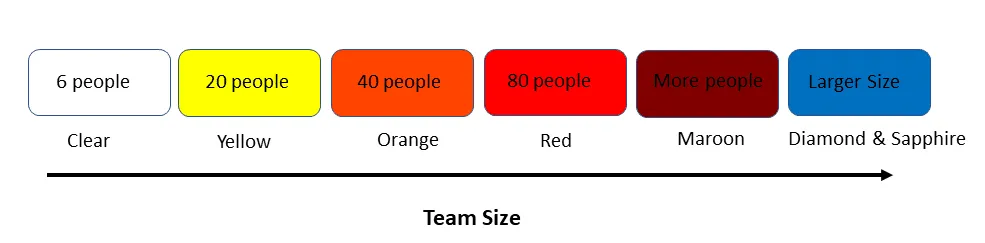
Upon observation, it appeared that the project properties like Criticality change with the number of people involved in the project.
Alistair observed that the small teams were able to build and deliver projects without much paperwork/status reports. Whereas the bigger teams, working on the big-scale projects, needed a lot of paperwork, continuous updates, and a lot of communication.
He found it depends on the project size of how complex the project is going to be. Therefore, he designed the Crystal method, which had different techniques for different project sizes.
He concluded that the suitability of the Crystal method depends on three dimensions:
· First, Team size
· Second, Criticality
· Third, the priority of the project
For example, a school divides its 5th class into various sections such as 5th A, 5th B, 5th C, on the basis on the following things-
Ø Their previous class scores
Ø Ability to understand
Ø Their strength
Dividing a class into sections helps teachers a lot. As the level of understanding is almost similar for all students, it allows teachers to define their teaching strategies accordingly.
Alistair used different colors to differentiate between different methods. Which, in turn, makes it easy to identify which way gets used when.
