What is Scaled Agile Framework(SAFe)? Learn in 5 Minutes
Scaled Agile Framework SAFe, is a freely available online knowledge base that allows you to apply lean-agile practices at the enterprise level. SAFe was first developed in the field and was elaborated in Dean Leffing well's books and blog. Version 1.0 is the first official release in 2011. The latest version is 4.0, was released in January 2016. It provides guidance to work at enterprise Portfolio, Value Stream, Program, and Team levels.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
- What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
- Why to use Agile Framework
- When to Use Scaled Agile Framework
- How different than other Agile practices
- Foundations of Scaled Agile Framework
- Agile Manifesto
- Different Levels in SAFE
· Team Level
· Program Level
· Portfolio Level
· Value Stream Level
What is Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
SAFe is an agile framework for software development. It provides a simple, lightweight experience for the development team. The whole framework is divided into three segments Team, Program and Portfolio. We will see this in detail later on. SAFe allows team for,
- Implementing Lean-Agile software and systems in enterprise level
- It's based on Lean and Agile principles.
- It gives detailed guidance for work at the enterprise Portfolio, Value Stream, Program, and Team.
- It's designed to meet the needs of all stakeholders within an organization.
Why to use Agile Framework
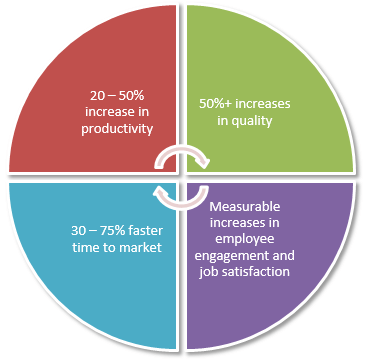
It is simpler and lighter in weight, yet it expands to handle the needs of large value streams and complex system development. By implementing Agile Framework, you will have following benefits,
- Productivity increased by 20 - 50%
- Quality increased more than 50%
- Time to Market is faster than 30 -75%
- Increased employee engagement and job satisfaction.
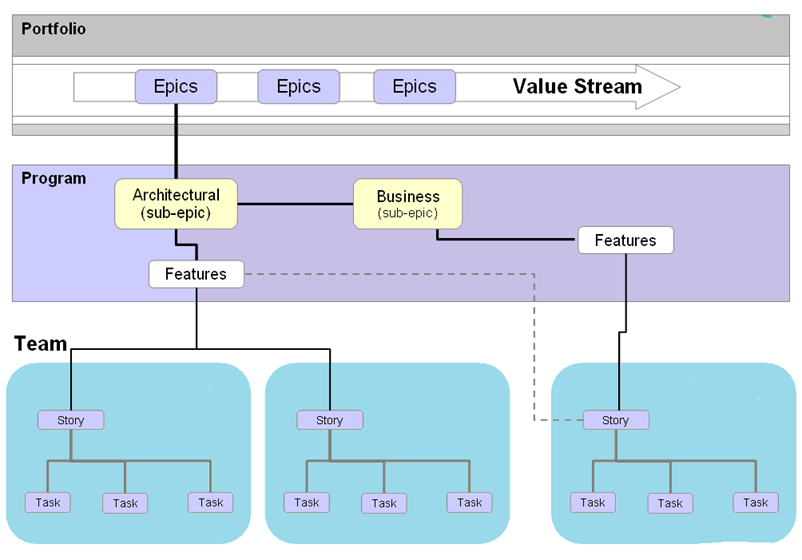
The detailed framework diagram is available on the website. It shows all of the key roles, Activities, deliverables and flows. It also serves as a navigational aid to the rest of the site.The below image explains how agile process works. Epics are a large body of work , which is further broken down into a number of smaller stories or sub-epics. These sub-epics are allocated to the team as a story. Each team then work on these stories or software features accordingly.
When to Use Scaled Agile Framework
- When a team is interested to implement agile approach consistently across larger, multi-team programs and portfolios.
- When multiple teams are running their own way of Agile implementation but regularly facing obstacles, delays, and failures .
- When teams want to work independently.
- When you want to scale Agile across the organization but not sure what new roles may be needed or what existing roles (i.e., management) need to change and how.
- When you have attempted to scale the Agile across your organization but struggling in alignment to achieve uniform or consistent strategy across business departments from portfolio to program and team levels.
- When an organization needs to improve its product development lead time and want to know how other companies have succeeded in scaling Agile with SAFe.
How different than other Agile practices
Let's see how Scaled Agile framework is different from other agile practices,
- It's publicly available and free to use.
- Available in a highly approachable and usable form.
- It's lightweight, practically proven results and specific to level.
- It constantly/regularly modifies/maintains most commonly used agile practices.
- Offers useful extensions to common agile practices.
- Grounds agile practices to an enterprise context.
- Offers complete picture of software development.
- Visibility or transparency is more on all the levels.
- Continues or regular feedback on quality and improvement.
Foundations of Scaled Agile Framework
Scaled Agile Framework(SAFe):
It stands on the foundations of its
- Lean-Agile Principles
- Core Values,
- Lean-Agile Leadership
- Lean-Agile Mind-set,
- Communities of Practice(Group of people who are constantly working on SAFe practices)
- Implementing 1-2-3
SAFe Lean Agile Principles
These basic principles and values for SAFe must be understood, exhibited and continued in order to get the desired results.
- Take an economic view
- Apply systems thinking
- Assume variability; preserve options
- Build incrementally with fast, integrated learning cycles
- Base milestones on objective evaluation of working systems
- Visualize and limit WIP, reduce batch sizes and manage queue lengths
- Apply cadence, synchronize with cross-domain planning
- Unlock the intrinsic motivation of knowledge workers
- Decentralize decision-making
SAFe Agile Core Values
The SAFe agile is based on these four values.
Alignment:
- SAFe supports alignment.
- Alignment starts at,
- Strategic Themes in Portfolio Backlog and
- Moves down to Vision and Roadmap of Program Backlogs and then
- Moves to the Team Backlogs.
Built-in Quality:
- It ensures that every incremental delivery reflects the quality standards.
- Quality is not "added later" is built in.
- Built-in quality is a prerequisite of Lean and its mandatory
Transparency:
- Transparency is the enabler for trust.
- SAFe helps the enterprise to achieve transparency at all levels- Executives, Portfolio Managers, and other stakeholders.
- Everyone can see into the portfolio backlog/Kanban, program backlogs/Kanban, and Team Backlog/Kanban.
- Each level has a clear understanding of the PI goals.
- Train Programs have visibility into the team's backlogs, as well other program backlogs
- Teams and programs have visibility into business and architecture Epics. They can see what might be headed their way.
Program Execution:
- SAFe places great focus on working systems and resultant business outcomes.
- SAFe is not useful if teams can't execute and continuously deliver value.
Lean Agile Leaders:
The Lean-Agile Leaders are lifelong learners and teachers. It helps teams to build better systems through understanding and exhibiting the Lean-Agile SAFe Principles.As an enabler for the teams, the ultimate responsibility is adoption, success and ongoing improvement of Lean-Agile developments. For the change and continuous improvement, leaders must be trained. Leaders need to adopt a new style of leadership. One that truly empowers and engages individuals and teams to reach their highest potential.
Principles of these Lean-Agile Leaders
- Lead the Change
- Know the Way; Emphasize Lifelong Learning
- Develop People
- Inspire and Align with Mission; Minimize Constraints
- Decentralize Decision-Making
- Unlock the Intrinsic Motivation of Knowledge Workers
Lean Agile Mind-Set:
Lean-Agile mindset is represented in two things:
- The SAFe House of Lean
- Agile Manifesto
The SAFe House of Lean:
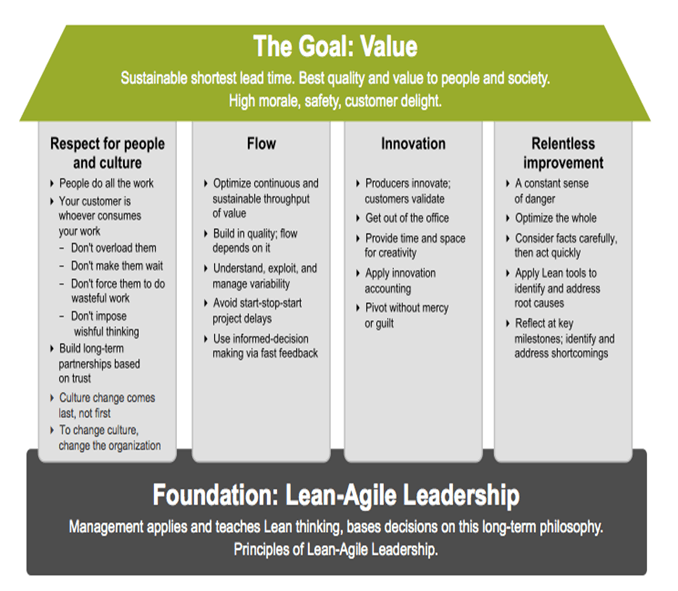
SAFe is derived from Lean manufacturing principles and practices. Based on these factors SAFe presents the "SAFe House of Lean". It is inspired by "house" of lean Toyota.The Goal of lean is unbeatable: To deliver maximum customer value in a shortest lead time with highest possible quality to customer Below figure explains the Goal, Pillars, and Foundation of "SAFe House of Lean."
Agile Manifesto
We are uncovering better ways of developing software by doing it and helping others do it. Through this work we have come to value:
That' why , while there is a value in the items on the right, we value the items on the left more.
Agile Manifesto
- The highest priority is to satisfy the customer through continuous and early delivery of valuable software.
- Embrace the changing requirements, even late in development. Agile processes harness change for the customer's benefit.
- Deliver working software frequently, from a couple of weeks to a couple of months, with a preference to the shorter timescale.
- Developers and business people must work together daily throughout the project.
- Build projects around motivated individuals. Give them support and the environment they need, and trust them to get the job done.
- The most efficient method for communication with a development team is a face-to-face conversation.
- Working software is the primary measure of progress.
- Agile processes promote sustainable development. The sponsors, developers, and users should be able to maintain a constant pace indefinitely.
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design enhances agility.
- Simplicity--the art of maximizing the amount of work not done--is essential.
- The best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams.
- At regular intervals, the team reflects on how to become more effective, then tunes and adjusts its behavior accordingly.
Different Levels in SAFE
There are two different types of SAFe implementation:
- SAFe 4.0 implementation
- SAFe 3.0 implementation
- In SAFe 4.0 implementation we have 4-Levels: Portfolio, Value Stream, Program, and Team.
- In SAFe 3.0 implementation we have 3-Levels: Portfolio, Program, and Team
- 3-Level SAFe is for smaller implementations with 100 or less people. Programs that do not require significant collaboration.
- 4-Level SAFe is for solutions that typically require many hundreds of practitioners to develop deploy and maintain software.
Team Level
|
Roles/Teams |
Events |
Artifacts |
||
|
* Agile Team |
* Sprint Planning |
* Team Backlog |
||
|
* Product Owner |
* Backlog Grooming |
* Non-Functional Requirements |
||
|
* Scrum Master |
* Daily Stand-Up |
* Team PI Objectives |
||
|
* Execution |
* Iterations |
|||
|
* Sprint Demo |
* Stories(Working Software) |
|||
|
* Sprint Retrospective |
* Sprint Goals |
|||
|
* IP Sprints |
* Built-In Quality |
|||
|
* Spikes |
||||
|
* Team Kanban |
- All SAFe teams are part of one or other Agile Release Train (ART).
- SAFe teams are empowered, self-organizing, self-managing, cross-functional teams
- Each team is equally responsible for defining, building and testing stories from their Team Backlog in a fixed-length Iterations
- Teams plan and execute two-week time boxed iterations in accordance with agreed-to Iteration Goals.
- Teams will use ScrumXP/Team Kanban routine to deliver high-quality systems to produce a System Demo on every two weeks.
- All different teams in the ART (Agile Release Trains) will create an integrated and tested system. Stakeholders will evaluate and respond with fast feedback
- They apply Built-in Quality practices.
- Each ScrumXP team will have 5-9 team members, which includes all the roles necessary to build a quality incremental value in each Iteration.
- ScrumXP roles includes:
- Team(Dev+QA)
- Scrum Master
- Product Owner. Etc..
- SAFe divides the development timeline into a set of iterations within a PI (Program Increment).
- PI duration is between 8 -12 weeks.
- The team will use stories to deliver the value. The Product Owner will have content authority over their creation and acceptance of the stories.
- Stories contain Customer's requirements.
- Team Backlog includes user and enabler stories, which are identified during PI planning. When the Product Management presents the Roadmap, Vision, and Program Backlog.
- Identifying, elaborating , prioritizing, scheduling, implementing, testing, and accepting the stories are the primary requirements of management work in team level.
- Each iteration provides:
- Valuable increment of new functionality
- Accomplish via constantly repeating pattern
- Plan the iteration
- Commit to some functionality
- Execute the iteration by building and testing Stories
- Demo the new functionality
- Retrospective
- Repeat for the next iteration
- Teams also support the System Demo at the end of each Iteration. which is the critical integration point for the ART.
- Larger Value Streams will have multiple ARTs.
- The Innovation and Planning (IP) Iterations leverage the teams with an opportunity for innovation and exploration.
Program Level
|
Roles/Teams |
Events |
Artefacts |
||
|
* DevOps |
* PI(Program Increment) Planning |
* Vision |
||
|
* System Team |
* System Demos |
* Roadmap |
||
|
* Release Management |
* Inspect and Adopt Workshop |
* Metrics |
||
|
* Product Management |
* Architectural Runway |
* Milestones |
||
|
* UEX Architect |
* Release Any Time |
* Releases |
||
|
* Release Train Engineer(RTE) |
* Agile Release Train |
* Program Epics |
||
|
* System Architect/Engineer |
* Release |
* Program Kanban |
||
|
* Business Owners |
* Program Backlog |
|||
|
* Lean-Agile Leaders |
* Non-Functional Requirements |
|||
|
* Communities of Practice |
* Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF) |
|||
|
* Shared Services |
* Program PI Objectives |
|||
|
* Customer |
* Feature |
|||
|
* Enabler |
||||
|
* Solution |
||||
|
* Value Stream Coordination |
- In Program level, Value of SAFe is delivered by long-lived Agile Release Trains (ART). Iteration is for team and train is for the program.
- Agile Release Trains (ART) is the primary vehicle for value delivery at the program level. It delivers a value stream to the organization.
- The Program Increments (PIs) duration is of 8 to 12 weeks.
- ART is of 5 - 12 Agile Teams (~50 – 125+ people) which includes all the roles and infrastructure needed to deliver fully tested, working, system-level software.
- Each PI is a multiple-Iteration time box. During which a significant, valuable increment of the system is developed and delivered.
- In each PI a "demo" and "Inspect and adapt" sessions will happen, and Planning begins for the next PSI.
- At the Program level, SAFe emphasis on the principle of alignment. This is because multiple agile team efforts are integrated to create customer value.
- SAFe artifact hierarchy is: Epics->features->user stories.
- At Program level, Product Manager/Program Manager has content authority. He defines and prioritizes the program backlog.
- Program backlog is a prioritized list of features.
- At the program level, features can be originated, or they can derive from epics defined at the portfolio level.
- Features decompose to user stories and flow into team-level backlogs.
- Product Manager or the Release Train Engineer role could be handled by Program Manager/Senior Project Manager
- System Architect role at the program level is to collaborate day to day work with the teams. It ensures that non-functional requirements are met. Also, they work with the enterprise architect at the portfolio level to make sure there is sufficient architectural runway to support upcoming user and business needs.
- Interface design, user experience guidelines and design elements for the teams are provided by UX Designers.
- Chief-Scrum Master role is played by 'Release Train Engineer'.
- Various team (from marketing, development, quality, operations and deployment) forms 'Release Management Team'. They will approve routine releases of quality solutions to customers.
- Deployment of software into customer environments and successful delivery is taken care by DevOps team.
Portfolio Level
|
Roles/Teams |
Events |
Artifacts |
||
|
* Enterprise Architect |
* Strategic Investment Planning |
* Strategic Themes |
||
|
* Program Portfolio Mgmt |
* Kanban Portfolio(Epic) Planning |
* Enterprise |
||
|
* Epic Owners |
* Portfolio Backlog |
|||
|
* Portfolio Kanban |
||||
|
* Non-Functional Requirements |
||||
|
* Epic and Enabler |
||||
|
* Value Stream |
||||
|
* Budgets(CapEX and OpEx) |
- Highest level of interest/ concern /involvement/ in SAFe is SAFe Portfolio
- The portfolio provides the basic blocks for organizing the Lean-Agile Enterprise flow of value via one or more Value Streams.
- The portfolio helps to develop systems and solutions which are described in strategic themes (links a SAFe portfolio to the changing business strategy of an enterprise).
- To meet strategic objectives, portfolio level encapsulates these elements. It provides the basic budgeting and other governance mechanisms. This way it assures that the investment in the value streams provides the returns necessary for the enterprise.
- Portfolio is connected to business bi-directionally:
- In order to guide the Portfolio to the larger changing business objectives, it provides strategic themes.
- Another direction indicates the constant flow of portfolio values.
- Program Portfolio Management acts as stakeholders, and they are accountable to deliver the business results.
- SAFe Portfolio Level contains: people , processes and necessary build systems and solutions that enterprise needs to meet its strategic objectives.
- Value Streams are the primary objectives in Portfolio, with which funding for the people and other resources required to build the Solutions.
- Important key concepts used here are:
- Connection to the Enterprise,
- Program Portfolio Management,
- Managing the Flow of Portfolio Epics.
Value Stream Level
|
Roles/Teams |
Events |
Artifacts |
||
|
* DevOps |
* Pre and Post PI(Program Increment) Planning |
* Vision |
||
|
* System Team |
* Solution Demos |
* Roadmap |
||
|
* Release Management |
* Inspect and Adopt Workshop |
* Metrics |
||
|
* Solution Management |
* Agile Release Train |
* Milestones |
||
|
* UEX Architect |
* Releases |
|||
|
* Value Stream Engineer(RTE) |
*Value Stream Epics |
|||
|
* Solution Architect/Engineer |
* Value Stream Kanban |
|||
|
* Shared Services |
* Value Stream Backlog |
|||
|
* Customer |
* Non-Functional Requirements |
|||
|
* Supplier |
* Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF) |
|||
|
* Value Stream PI Objectives |
||||
|
* Capability |
||||
|
* Enabler |
||||
|
* Solution Context |
||||
|
* Value Stream Coordination |
||||
|
* Economic Framework |
||||
|
* Solution Intent |
||||
|
* MBSE |
||||
|
* Set Based |
||||
|
* Agile Architecture |
- The Value Stream Level is optional in SAFe.
- Value Stream Level is new in SAFe 4.0.
- The Value Stream Level is intended/designed for Enterprises /builders/organization who are:
- Large in size
- Independent
- Have complex solutions
- Their solutions typically require multiple ARTs
- They have Suppliers contribution.
- They face the largest systems challenges
- For cyber-physical systems
- For software, hardware, electrical and electronic, optics, mechanics, fluidics and more.
- Building this kind of systems often takes hundreds, even thousands of practitioners, external and internal suppliers.
- If the systems are mission crucial. Failure of the Solution, or even a subsystem, has unacceptable economic and social consequences.
- If the Enterprises can be built with a few hundred practitioners, it may not need the constructs of this level. In that case, they can use from the 'collapsed view' which is 3-level SAFe.
- Building value stream solutions in a Lean-Agile pattern requires additional artifacts, coordination, and constructs. So this level contains an Economic Framework to provide financial boundaries for Value Stream
- It supports cadence and synchronization for multiple ARTs and Suppliers. It includes Pre-and Post-PI Planning meetings and Solution Demo.
- It gives additional roles which are: Value Stream Engineer, Solution Architect/Engineering, and Solution Management.
Summary:
- SAFe is an industry-proven, value-focused method for scaling Agile at the Enterprise level.
- It answers the questions like "How do we plan?", "How do we budget?", and "How do we become cross-functional in architecture and DevOps?"
- SAFe helps large organization teams to meet organization's strategic goals, not just individual project goals.
- The framework offers the ability to maintain and create a centralized strategy to deliver value.
- The SAFe model has three/four levels that centralize the strategic themes of an organization.
- Centralized strategy, combined with the de-centralized agile development execution.