Scrum Testing Beginners Tutorial: Roles, Artifacts, Ceremonies
What is Scrum?
Building complex software applications is a difficult task. Scrum methodology comes as a solution for executing such complicated task. It helps development team to focus on all aspects of the product like quality, performance, usability and so on.
Following are Key Features of Scrum-
- Scrum has short fixed schedule of release cycles with adjustable scope known as sprints to address rapidly changing development needs. Each release could have multiple sprints. Each Scrum Project could have multiple Release Cycles.
- A repeating sequence of meetings, events and milestones
- A practice of testing and implementing new requirements, known as stories, to make sure some work is released ready after each sprint Scrum is based on following 3 Pillars-
Let's look at the one by one
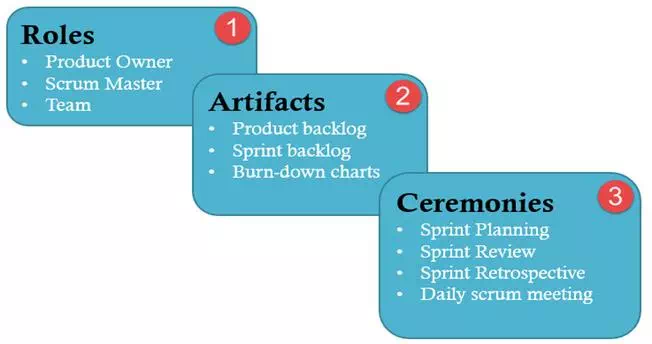
Roles in Scrum
There are three chief roles in Scrum Testing – Product Owner, Scrum Master and The Development Team. Let's study them in detail
|
Product Owner |
Scrum Master |
The Team |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Scrum Artifacts
A scrum process includes
- User stories: They are short explanation of functionalities of the system under test. Example for Insurance Provider is – "Premium can be paid using the online system."
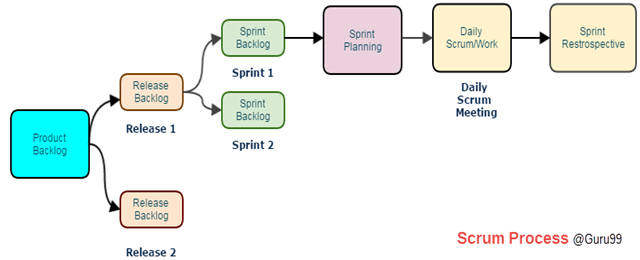
- Product Backlog: It is a collection of user stories captured for a scrum product. The product owner prepares and maintains the product backlog. It is prioritized by product owner, and anyone can add to it with approval from the product owner.
- Release Backlog: A release is a time frame in which the number of iterations is completed. The product owner co-ordinates with the scrum master to decide which stories should be targeted for a release. Stories in the release backlog are targeted to be completed in a release.
- Sprints: It is a set period of time to complete the user stories, decided by product owner and developer team, usually 2-4 weeks of time.
- Sprint Backlog: It's a set of user stories to be completed in a sprint. During sprint backlog, work is never assigned, and the team signs up for work on their own. It is owned and managed by the team while the estimated work remaining is updated daily. It is the list of task that has to be performed in Sprint
- Block List: It is a list of blocks and unmade decisions owned by scrum master and updated daily
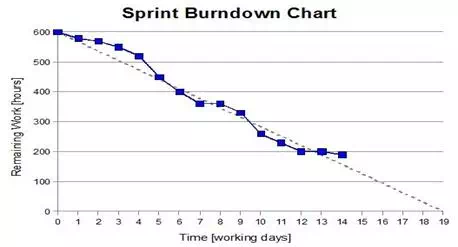
- Burndown chart: Burn-down chart represents overall progress of the work in progress and work completed throughout the process. It represents in a graph format the stories and features not completed
Ceremonies (Processes) in Scrum
- Sprint Planning: A sprint begins with the team importing stories from the release backlog into the sprint backlog; it is hosted by scrum master. The Testers estimate effort to test the various stories in the Sprint Backlog.
- Daily Scrum: It is hosted by scrum master, it last about 15 minutes. During Daily Scrum, the members will discuss the work completed previous day, the planned work for the next day and issues faced during sprint. During daily stand-up meeting team progress is tracked.
- Sprint Review/ Retrospective: It is also hosted by scrum master, it last about 2-4 hours and discuss what team has accomplished in the last sprint and what lessons were learned.
Role of Tester in Scrum
There is no active role of Tester in Scrum Process. Usually, testing is carried out by developer with Unit Test. While product owner is also frequently involved in the testing process during each sprint. Some Scrum projects do have dedicated test teams depending on the nature & complexity of the project.The next question is, what tester do in scrum? Following note will answer Testing Activities in Scrum Testers do following activities during the various stages of Scrum-
Sprint Planning
- In sprint planning, tester should pick a user-story from the product backlog that should be tested.
- As a tester, he/she should decide how many hours (Effort Estimation) it should take to finishtesting for each of selected user stories.
- As a tester, he/she must know what sprint goals are.
- As a tester, contribute to the prioritizing process
Sprint
- Support developers in unit testing
- Test user-story when completed. Test execution is performed in a lab where both tester and developer work hand in hand. Defect are logged in Defect Management tool which are tracked on a daily basis. Defects can be conferred and analyzed during scrum meeting. Defects are retested as soon as it is resolved and deployed for testing
- As a tester, he/she attends all daily standup meeting to speak up
- As a tester, he/ she can bring any backlog item that cannot be completed in the current sprint and put to the next sprint
- Tester is responsible for developing automation scripts. He schedules automation testing with Continuous Integration (CI) system. Automation receives the importance due to short delivery timelines. Test Automation can be accomplished by utilizing various open source or paid tools available in the market. This proves effective in ensuring that everything that needs to be tested was covered. Sufficient Test coverage can be achieved with a close communication with the team.
- Review CI automation results and send Reports to the stakeholders
- Executing non-functional testing for approved user stories
- Coordinate with customer and product owner to define acceptance criteria for Acceptance Tests
- At the end of the sprint, tester also does acceptance testing(UAT) in some case and confirms testing completeness for the current sprint
Sprint Retrospective
- As a tester, he will figure out what went wrong and what went right in the current sprint
- As a tester, he identifies lesson learned and best practices
Test Reporting
Scrum Test metrics reporting provides transparency and visibility to stakeholders about the project. The metrics that are reported allow team to analyze their progress and plan their future strategy to improve the product. There are two metrics that are frequently used to report.
Burn down chart: Each day, Scrum Master records the estimated remaining work for the sprint. This is nothing but the Burn Down Chart. It is updated daily.A burndown chart gives a quick overview of the project progress, this chart contains information like total amount of work in the project that must be completed, amount of work completed during each sprint and so on.
Velocity history graph: The velocity history graph predicts the velocity of the team reached in each sprint. It is a bar graph and represents how teams output has changed over time.The additional metrics that may be useful are schedule burn, budget burn, theme percent complete, stories completed - stories remaining and so on.Do you have any tips or experiences to share for Scrum Testing? Do leave a comment below-