Newton's Theory of Flight
Isaac Newton did not propose a theory of flight but he did provide Newton's Laws of Motion the physical laws which can be used to explain aerodynamic lift.
Newton's Second Law states that:
· The force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration or equivalently to its rate of change of momentum
F = M a = d/dt (M v)
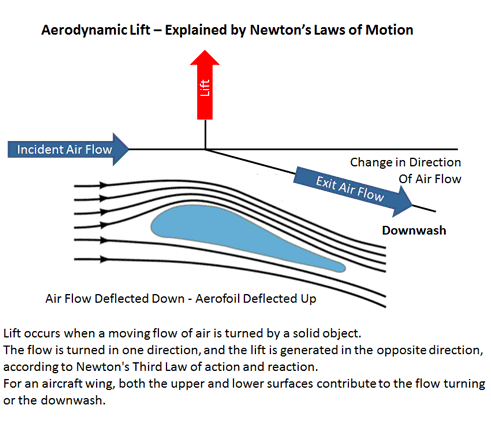
In other words, whenever there is a change of momentum, there must be a force causing it. In this case, since momentum is a vector quantity, the change in direction of the airflow around the wing must be associated with a force on the volume of air involved.
Newton's Third Laws states that:
· To every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
This means that the force of the aerofoil pushing the air downwards, creating the downwash, is accompanied by an equal and opposite force from the air pushing the aerofoil upwards and hence providing the aerodynamic lift.
It is thus the turning of the air flow which creates the lift.
