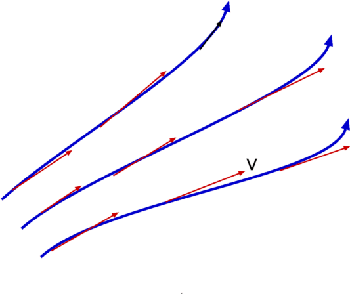
Figure 3.5 : Streamlines
Flow Description, Streamline, Pathline, Streakline and Timeline
Streamline, pathline, streakline and timeline form convenient tools to describe a flow and visualise it. They are defined below.

Figure 3.5 : Streamlines
Figure 3.6: Streamline definition
A streamline is one that drawn is tangential to the velocity vector at every point in the flow at a given instant and forms a powerful tool in understanding flows. This definition leads to the equation for streamlines.
where u,v, and w are the velocity components in x, y and z directions respectively as sketched.
Figure 3.7 : Streamtube
Hidden in the definition of streamline is the fact that there cannot be a flow across it; i.e. there is no flow normal to it. Sometimes, as shown in Fig.3.7 we pull out a bundle of streamlines from inside of a general flow for analysis. Such a bundle is called stream tube and is very useful in analysing flows. If one aligns a coordinate along the stream tube then the flow through it is one-dimensional.
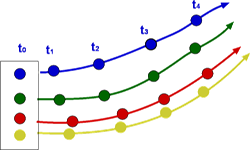
Figure 3.8: Pathlines
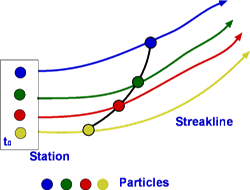
Figure 3.9: Streaklines Figure 3.10: Timeline
Pathline is the line traced by a given particle. This is generated by injecting a dye into the fluid and following its path by photography or other means (Fig.3.8). Streakline concentrates on fluid particles that have gone through a fixed station or point. At some instant of time the position of all these particles are marked and a line is drawn through them. Such a line is called a streakline (Fig.3.9). Timeline is generated by drawing a line through adjacent particles in flow at any instant of time. Fig.3.10 shows a typical timeline.