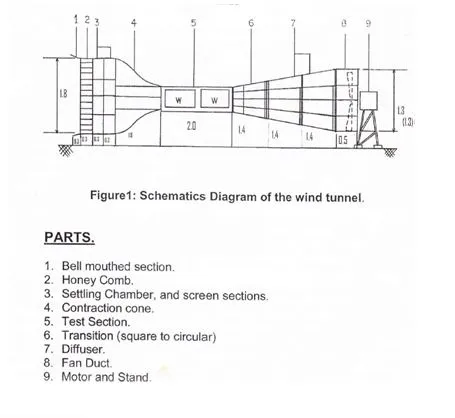
Wind Tunnel Fundamentals
A wind tunnel is a tool used in aerodynamic research to study the effects of air moving past solid objects. A wind tunnel consists of a tubular passage with the object under test mounted in the middle. Air is made to move past the object by a powerful fan system or other means. The test object, often called a wind tunnel model is instrumented with suitable sensors to measure aerodynamic forces, pressure distribution, or other aerodynamic-related characteristics.Airfoil performance at low Reynolds numbers impacts the performance of a wide range of systems. Low Reynolds number aerodynamics of airfoils apply to a host of other applications such as wind turbines, motorsports, high altitude aircraft and propellers, natural flyers, and subscale testing of many full scale systems. Accurate measurements of low Reynolds number airfoil performance arekey to understanding and improving the efficiency of low Reynolds number systems. Most aerodynamic performance measurement techniques for airfoils rely on using balance systems or pressure systems, or a combination of both. The approach described here uses a force balance approach to obtain lift and moment data and the wake rake method to obtain drag.
