Block Diagram Reduction
Follow these rules for simplifying (reducing) the block diagram, which is having many blocks, summing points and take-off points.
· Rule 1 − Check for the blocks connected in series and simplify.
· Rule 2 − Check for the blocks connected in parallel and simplify.
· Rule 3 − Check for the blocks connected in feedback loop and simplify.
· Rule 4 − If there is difficulty with take-off point while simplifying, shift it towards right.
· Rule 5 − If there is difficulty with summing point while simplifying, shift it towards left.
· Rule 6 − Repeat the above steps till you get the simplified form, i.e., single block.
Note − The transfer function present in this single block is the transfer function of the overall block diagram.
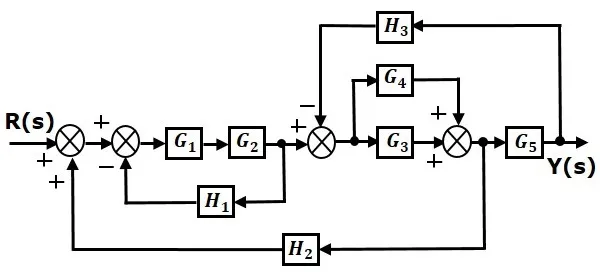
Consider the block diagram shown in the following figure. Let us simplify (reduce) this block diagram using the block diagram reduction rules.

Step 1 − Use Rule 1 for blocks G1G1 and G2G2. Use Rule 2 for blocks G3G3 and G4G4. The modified block diagram is shown in the following figure.
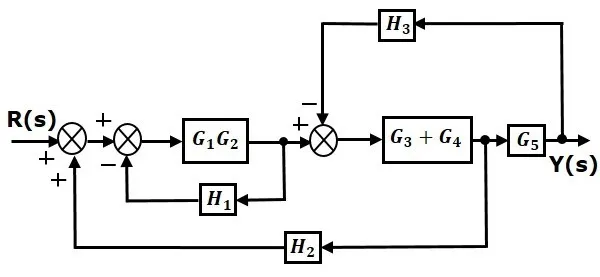
Step 2 − Use Rule 3 for blocks G1G2G1G2 and H1H1. Use Rule 4 for shifting take-off point after the block G5G5. The modified block diagram is shown in the following figure.
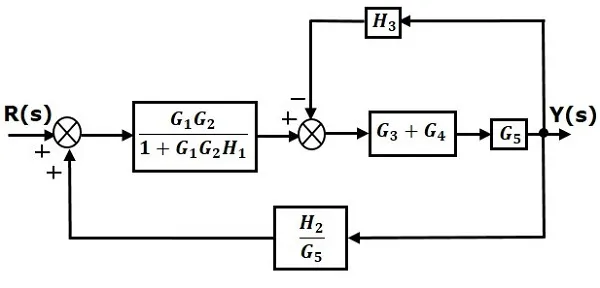
Step 3 − Use Rule 1 for blocks (G3+G4)(G3+G4) and G5G5. The modified block diagram is shown in the following figure.
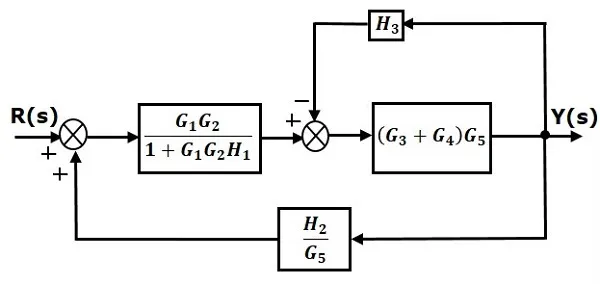
Step 4 − Use Rule 3 for blocks (G3+G4)G5(G3+G4)G5 and H3H3. The modified block diagram is shown in the following figure.
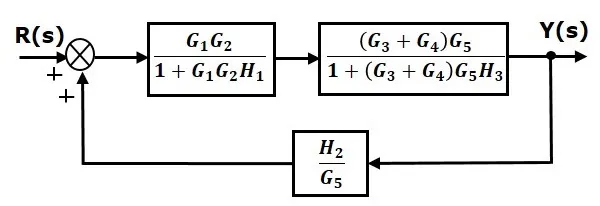
Step 5 − Use Rule 1 for blocks connected in series. The modified block diagram is shown in the following figure.
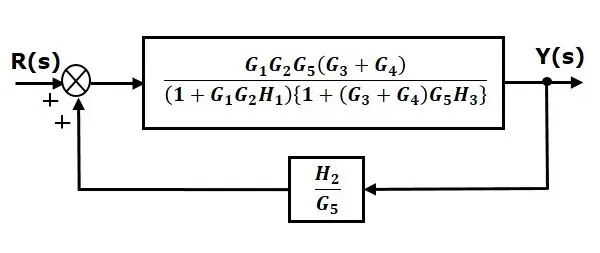
Step 6 − Use Rule 3 for blocks connected in feedback loop. The modified block diagram is shown in the following figure. This is the simplified block diagram.
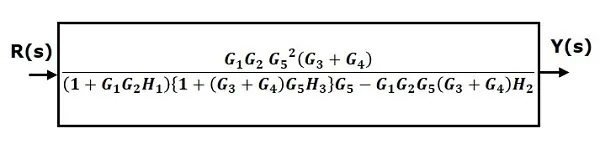
Therefore, the transfer function of the system is
