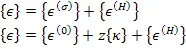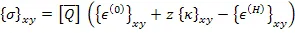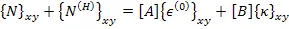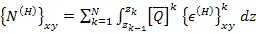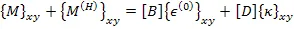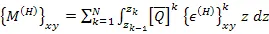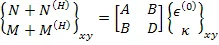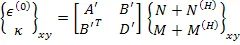Laminate Theory with Hygral Effects:
In this study, the total strain is assumed to be superimposition of mechanical and hygral strains.
| (5.113) |
where, ![]() is the hygral strain in laminate. The stress in global direction is given as
is the hygral strain in laminate. The stress in global direction is given as
| (5.114) |
The resultant in-plane forces are given as
| (5.115) |
where,
| (5.116) |
is defined as the resultant in-plane forces per unit length due to hygral strains.
In a similar way, we can give the resultant moments as
| (5.117) |
where,
| (5.118) |
is defined as resultant moments per unit length due to hygral strains. Combining Equation (5.116) and Equation (5.118), we write
| (5.119) |
The inverse of this equation is written as
| (5.120) |