What Is Market Price? Pinpointing Where Supply Meets Demand
Knowing the market price for products or services is key to knowing how to get a deal, increase sales, and grow your business. And when it comes to running your company, you likely participate in different markets to provide your goods or services. Depending on your offerings and industry, your businessís market price may vary. So, what is market price?
What is market price?
Market price is the amount a product or service can be bought or sold for. You can find market price when supply meets demand. To find market price, balance supply and consumer demand. When supply and demand shift or fluctuate, market price can also change.
Equilibrium and market clearing price describe where supply and demand meet.
Why market price can change
There are two main reasons why you might reevaluate market price, including:
1. If thereís a decrease in product or service availability
2. If product or service availability increases
When thereís a decrease in the availability of a good or service, consumers tend to agree to pay more because itís in demand. Because the rarity of the product or service increases, items become more valuable to the market and consumers.
The opposite occurs when availability increases for products and services. When products and services are easier to obtain, consumers typically refuse to pay higher prices for them. If consumers know they can easily access a good or service, they will likely purchase it elsewhere at a lower cost.
If either of the two scenarios occurs, businesses should adjust prices accordingly to meet the changes in supply and demand.

Factors that impact market price
Although the principle of market price ultimately depends on supply and demand, there are a number of factors that can also affect market price.
Some things that can affect market price are controllable, while others are out of your hands. Factors that impact market price include:
∑ Natural disasters
∑ World events
∑ Amount of wages paid to workers
∑ Decrease or increase in employment
∑ Pricing of luxury items versus necessities
Natural disasters or other world events (e.g., wars or attacks) can limit supplies to manufacturers. Decreases in necessary supplies can slow down the production of goods or a businessís ability to offer services. And if thereís a deficit in products or services, demand can increase due to limitations.
Employment and the wages paid to workers can also affect the equilibrium price. A decrease in employment or wages may cause consumers to penny pinch. And, consumers might not afford to pay the same prices as before.
Likewise, an increase in jobs and wages results in consumers being able to pay more, allowing for higher market prices for goods and services.
Market prices of luxury items have different equilibriums than basic necessities, like food. And, luxury products and services break the basic rules of supply and demand. Although the demand for luxury items is smaller, the prices are almost always high. Rarity does not impact the price of the luxury item. Instead, consumers are willing to pay more for name brands and quality.
How to find market price
To determine market price, find where supply equals demand. Find market price by researching things like market trends, and the number of suppliers and existing buyers.
Calculating market price can be challenging because it doesnít use regular business formulas.
Simplify the way you find market price by creating a graph. Once you craft your graph, find the point where the demand and supply lines meet to determine market price.
In some cases, the numbers for supply and demand may be a range rather than a single number or area on your graph.
Take a look at an example of a market price graph below.
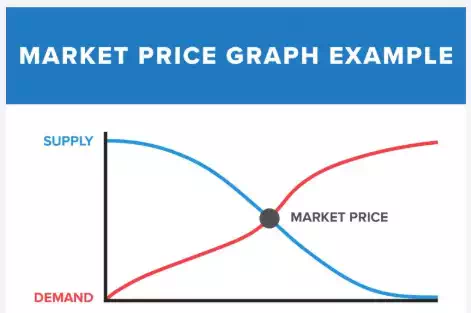
Balancing market price
The forces of supply and demand are always changing. Market price is a constant balancing act for small business owners. If any changes occur from either side of the market, make adjustments to things like supplies and prices.
Manufacturers, retailers, and service providers want high market prices because they encourage more production to boost profits and business revenue.
Consumers typically prefer lower market prices to stretch their dollars.
Market price and stocks
Market price can also be associated with the stock market. The market price per share of stock, or the share price, is the amount investors are willing to pay for one share of a companyís stock.
The interaction between sellers and buyers determines the market price for stocks. Sellers and buyers help determine the supply and demand for stocks. If thereís more demand for a certain stock, the market price likely increases.