Sources of redemption
From the point of view of sources redemption may be carried out with the help of any of the following sources:
1. Out of capital,
2. Out of profits,
3. Conversion or rollover (already discussed), and
4. Out of provision in the nature of sinking fund.
We shall now consider each case
Redemption out of capital
SEBI guidelines require the setting up of a ‘Debenture Redemption Reserve when profits are available and the debentures are issued for a period beyond 18 months. If the debentures are for a period less than 18 months or profits are not available for capital redemption, debentures may be redeemed from out of capital. When redemption is carried from out of capital only entries are made for redemption and no entry will be made to transfer profits to ‘Debenture Redemption Reserve.
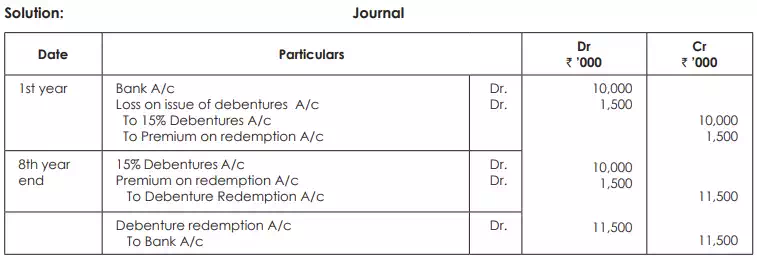
A company issued 100,000 15% debentures of ` 100 each at par redeemable at a premium of 15%. After 8 years the company served notice of redemption and redeemed all debentures as per the terms of issue. You are required to make entries at the time of issue and at the time of redemption.
Redemption from out of Profits
Now it is mandatory to set up ‘Debenture Redemption Reserve’. Earlier companies could redeem debentures from out of profits without a formal setting up of ‘Debenture Redemption Reserve’. It was the directors who used to decide as to whether the redemption is from capital or profits. After carrying out the entire redemption the amount to the credit of debenture redemption reserve will be transferred to general reserve account.
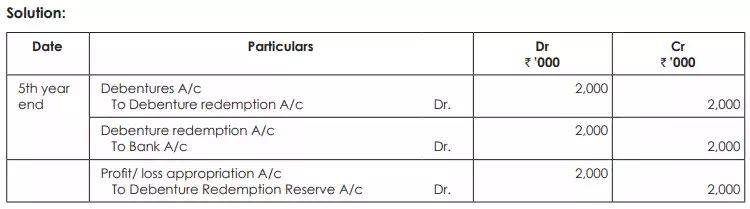
A Company issued 100,000 debentures of ` 100 each redeemable at the end of 10th year, but reserves the right to redeem earlier from the end of 5th year. The company decides at the end of 5th year to redeem 20,000 debentures out of profits it has made. Pass necessary journal entries relating to redemption?
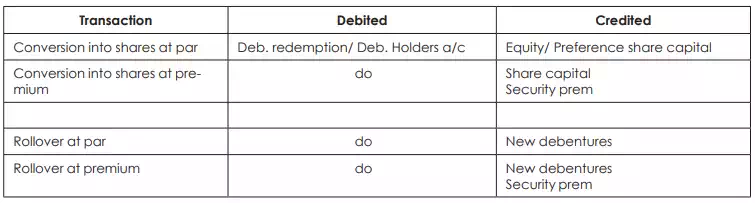
Conversion or rollover
In the case of conversion debentures are converted into equity or preference shares. In the case of rollover old debentures or replaced by the issue of new debentures. The new shares may be issued at par or premium.
Additional accounting entries for conversion or rollover are as below:
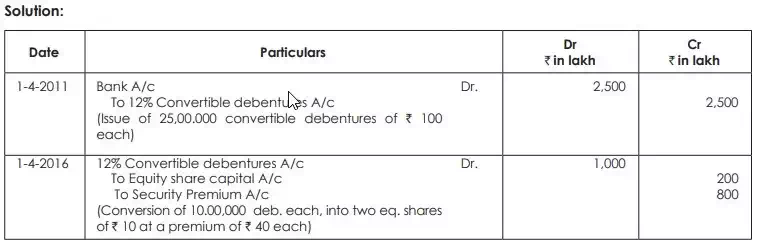
On April 1, 2011 PT Ltd. issued 25,00,000 12% fully convertible debentures of ` 100 each at par. The debenture holders were given the call option to convert the debentures into ` 10 equity shares at a premium of ` 40 per share on or after July 1, 2015. On April 1, 2016, debenture holders holding 10,00,000 debentures exercised their option. Pass the necessary journal entries.
When to be redeemed?
Time of redemption can be classified in the following three ways: 1. Redemption by annual drawings even before the maturity of debentures. 2. Purchases of debentures from the open market and canceling them immediately or later. 3. Redemption only on maturity.
Redemption by Annual Drawings
SEBI guidelines state that the issuing company shall redeem the debentures as per the offer document. A company at the time of issue may provide for staggered redemption. This can be done in two ways. The redemption may be certain amount of each debenture with a schedule so that redemption may be completed over a time frame. The other way is to select certain number of debentures every year and redeem them fully. The debentures to be redeemed are selected by drawing a lot annually. This method is known as ‘Redemption by Annual Dr. awings’. Again whether the redemption is at par, premium or discount, depend on the terms of offer. nowadays it is also common for companies to have a call option which gives them the right to redeem the debentures at a pre-determined price. This gives them the right to cancel but not the obligation to cancel.
Purchase and Cancellation of Own Debentures
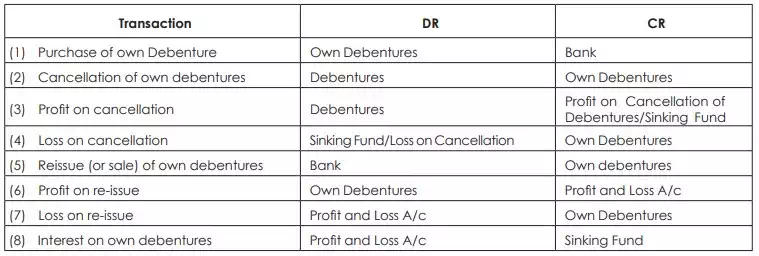
Debentures may also be cancelled before the expiry of the period by purchasing them from the open market at market price, which may be at premium or discount to the book value. It is certainly advantageous to buy when they are selling in the market at a discount. Cancellation of debentures may be done immediately or later. In some cases such debentures may also be reissued. This method of redemption is known as ‘purchase and cancellation of own debentures’. For purchase and cancellation of own debentures, the company have to consider the following parameters.
1. The company may cancel such debentures immediately or carry them as an investment and cancel at a later date.
2. Where they are immediately cancelled, a debenture liability is extinguished to the extent of par value of the debentures cancelled. From the date of cancellation, interest is not payable on cancelled debentures.
3. Since the debenture liability cancelled is more than the amount paid for such debentures, profit on cancellation of debentures should be recorded. If there is a Sinking Fund, such profit is transferred to the Sinking Fund.
4. When debentures are carried as an investment, debenture liability is shown as before and at the same time, ‘Investment in own Debentures’ or simply ‘Own Debentures’ appears on the assets side of the balance sheet, till they are cancelled.
5. In the case of own debentures, interest on own debentures must be reckoned as income or set-off against the gross interest payable on the whole of debentures. 6. If debentures are purchased between two interest dates, and not immediately after payment of interest, then the price paid for debentures depends on the quotation.
Accounting Entries
Sinking Fund Method
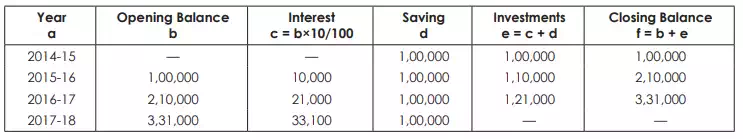
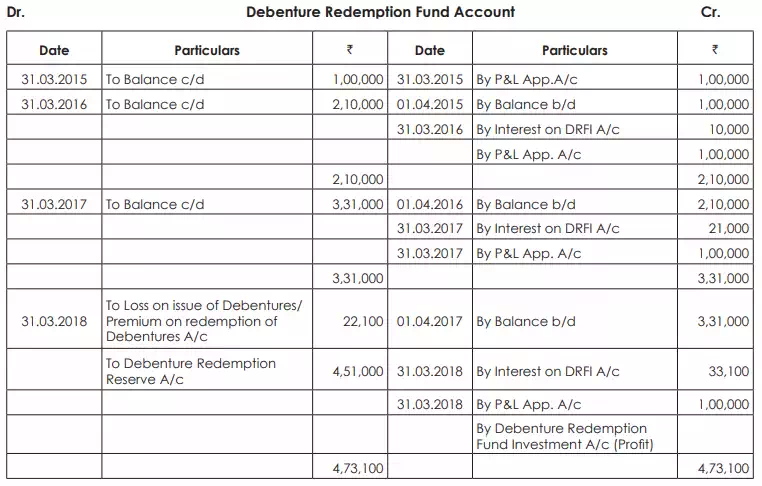
On 1st April 2014. H Ltd. issued 442, 10% Debentures of ` 1000 each at a discount of 10% redeemable at a premium of 5% after 4 years. It was decided to create a Sinking Fund for the purposes of accumulating sufficient funds to redeem the Debentures and to invest in some radily convertible securities yielding 10% interest p.a. Reference to the table shows that ` 1.00 p.a. at 10% compound interest amounts to ` 4.641 in 4 years. Investments are to be made in the Bonds of ` 1000 each available at par.
On 31st March 2018, the investments realised ` 3,40,000 and debentures were redeemed. The bank balance as on that date was ` 50,000. Required:
Prepare Debenture Redemption Fund Account and Debenture Redemption Fund Investments Account for 4 years.
DRF = Debenture Redemption Fund, DRFI = Debenture Redemption Fund Investment.

Working Note:
(i) Calculation of the amount of profit set aside

(ii) Calculation of the amount of investments and interes