Accounts For Non-Profit Making Organisations
Introduction
Non-profit making organisations, also known as non-trading institutions or organisations, include such voluntary associations of persons as are formed for the purpose of providing recreational facilities to its members or to promote art, culture, education, commerce, science, religion and other social and charitable purposes. There is no purchase or manufacture of goods for trading purposes in these non-profit making organisations. The primary object of these institutions is to render a service to their members (or society) or to satisfy membersí common needs. The examples of such organisations include sport clubs, educational institutions, hospitals, libraries, temples, churches, gurudwaras, masjids. Similarly, the associations of manufacturers or traders and professionals are also non-profit making organisations and include medical councils, bankers association, teachers association, The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, The Institute of Cost and Works Accountants of India, The Institute of Company Secretaries of India. All these entities are formed for the purpose of promotion and protection of their professional interests. The non-trading organisations too like trading organisations have to prepare the financial statements at the end of the accounting year. The non-trading institutions are different from the trading institutions in several respects. They have not to purchase and sell goods, accept or receive bills of exchange nor do they have too many credit transactions. Most of their transactions are cash transactions and, therefore, they need not maintain as many books of accounts as trading institutions have to maintain. However, they do maintain a cash book and minimum number of such other books which may be required for their purposes. For example, a Register of Members, a Minute Book are maintained in case of a club or a society, a student fee register is maintained in case of a school or a college, a summary record of outstanding fees may be kept by an Advocate or a Chartered Accountant.
At the end of the accounting period, a non-trading institution also prepares its final accounts, which include the following:
(i) Receipts and Payments Account,
(ii) Income and Expenditure Account, and
(iii) Balance Sheet.
Receipts And Payments Account
Receipts and Payments Account is a summary of cash transactions for a given period. All the receipts, by cash or by cheque, are entered on the debit side, whereas all the payments, by cash or by cheque, are shown on the credit side. It begins with an opening balance (Cash or/and Bank) and is debited with all the items of receipts irrespective of whether they are of capital or revenue nature or whether they pertain to the accounting period or not. The payments are recorded on the credit side without making any distinction between items of capital and revenue nature and irrespective of the fact whether they belong to the accounting period or not. Moreover, this account is not used to record outstanding items of receipts and payments since these are non-cash items. At the end of the accounting period, this account is balanced to ascertain the balance of cash in hand or at the bank or the overspent amount or bank overdraft.
Features
The main features of the Receipts and Payments Account can be summarised as follows:
(a) It is a real account, i.e., it is a summarised copy of cash receipts and cash payments.
(b) Itís form is similar to Cash Book (without discount and bank columns) with debit and credit sides. Receipts are recorded on the debit side while payments being entered on the credit side.
(c) It records all receipts and payments irrespective of the distinction between capital and revenue items. In other words, both capital and revenue receipts and payments are included.
(d) Only actual receipts and payments during the accounting period, whether relating to previous or current or succeeding years are recorded in it.
(e) The opening and closing balances in it mean cash in hand/bank in the beginning and at the end, respectively. The balance of Receipts and Payments Account must be debit being cash on hand and/or at bank, unless there is a bank overdraft.
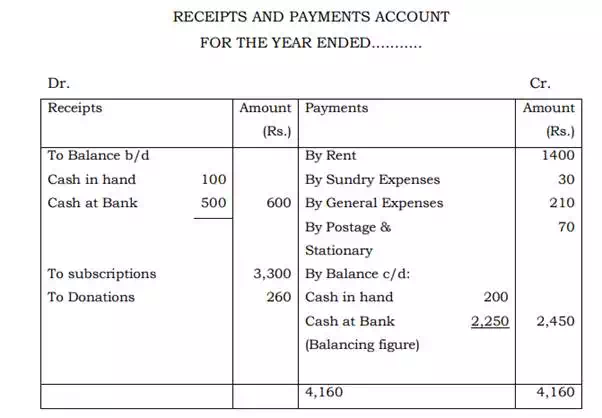
Illustration: From the following particulars taken from the Cash Book of a Club, prepare a Receipts and Payments Account.
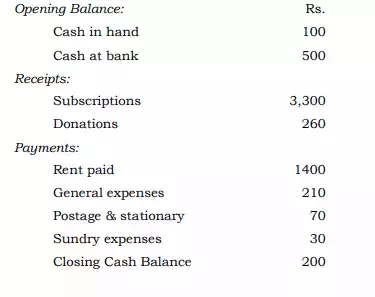
Solution